For example:
Lets say if battery temperature is too high, you may want to close some application.
In this post, we are going to see how to get current battery temperature in android.
Source code:
Step 1 :
Create an android application project named “GetBatteryTemperatureApp”.
Step 2 :
Change res ->layout -> activity_main.xml as below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/activity_main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.java2blog.getbatterytemperatureapp.MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textViewBatteryTemp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" /> <Button android:id="@+id/buttonBatteryTemp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/textViewBatteryTemp" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:text="Click here to Get battery temperature" /> </RelativeLayout> |
Step 3:
Change src/main/packageName/MainActivity.java as below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 |
package com.java2blog.getbatterytemperatureapp; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.IntentFilter; import android.os.BatteryManager; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView; import com.java2blog.getbatterytemperatureapp.R; public class MainActivity extends Activity { TextView tempTextView; Button button; IntentFilter intentfilter; float batteryTemp; String currentBatterytemp="Current Battery temp :"; int batteryLevel; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.buttonBatteryTemp); tempTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textViewBatteryTemp); intentfilter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED); button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { MainActivity.this.registerReceiver(broadcastreceiver,intentfilter); } }); } private BroadcastReceiver broadcastreceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { batteryTemp = (float)(intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_TEMPERATURE,0))/10; tempTextView.setText(currentBatterytemp +" "+batteryTemp +" "+ (char) 0x00B0 +"C"); } }; } |
As we want to get battery level change information, we need to register broadcast receiver and intent filter. An intent filter is used to tell native battery app that this app is listening for changes in native battery app.
Lets understand above code:
Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED:
If you see the code we have used Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED to get current battery info. It is sticky broadcast which contain battery charging state , level and other info. BatteryManager class contains all constant strings.
Sticky broadcast is broadcast which will remain active once registered.
|
1 2 3 |
MainActivity.this.registerReceiver(broadcastreceiver,intentfilter); |
Here we are registering created broadcastreceiver to the MainActivity and intent filter is listening for battery change events.
Run the app:
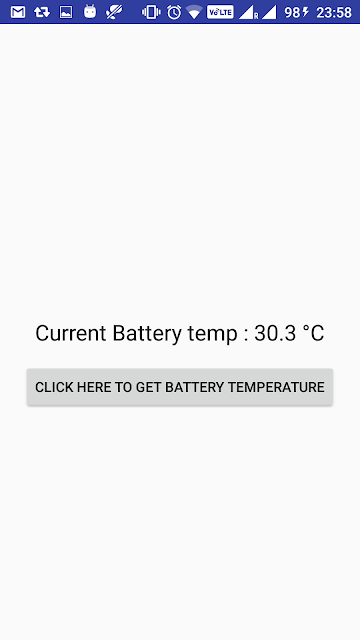
When you run above app on actual device, you will get below screen :