Target Audience
This Spring tutorial is designed for Java programmers who need to understand the Spring framework and its application.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this Spring tutorial you should have a good understanding of the Java programming language.
Introduction
Further reading:
Features
-
Lightweight
spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 1MB. And the processing overhead is also very negligible.
-
Inversion of control (IOC)
The basic concept of the Dependency Injection or Inversion of Control is that, programmer do not need to create the objects, instead just describe how it should be created. No need to directly connect your components and services together in program, instead just describe which services are needed by which components in a configuration file/xml file. The Spring IOC container is then responsible for binding it all up. -
Aspect oriented (AOP)
Spring supports Aspect oriented programming .
Aspect oriented programming refers to the programming paradigm which isolates secondary or supporting functions from the main program’s business logic. AOP is a promising technology for separating crosscutting concerns, something usually hard to do in object-oriented programming. The application’s modularity is increased in that way and its maintenance becomes significantly easier. -
Container
Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects. -
MVC Framework
Spring comes with MVC web application framework, built on core Spring functionality. This framework is highly configurable via strategy interfaces, and accommodates multiple view technologies like JSP, Velocity, Tiles, iText, and POI. But other frameworks can be easily used instead of Spring MVC Framework. -
Transaction Management
Spring framework provides a generic abstraction layer for transaction management. This allowing the developer to add the pluggable transaction managers, and making it easy to demarcate transactions without dealing with low-level issues. Spring’s transaction support is not tied to J2EE environments and it can be also used in container less environments. -
JDBC Exception Handling
The JDBC abstraction layer of the Spring offers a meaningful exception hierarchy, which simplifies the error handling strategy. Integration with Hibernate, JDO, and iBATIS: Spring provides best Integration services with Hibernate, JDO and iBATIS
Architecture
Spring is well-organized architecture consisting of seven modules. Modules in the Spring framework are:
-
Spring AOP
One of the key components of Spring is the AOP framework. AOP is used in Spring:
- To provide declarative enterprise services, especially as a replacement for EJB declarative services. The most important such service is declarative transaction management, which builds on Spring’s transaction abstraction.
- To allow users to implement custom aspects, complementing their use of OOP with AOP
-
Spring ORM
The ORM package is related to the database access. It provides integration layers for popular object-relational mapping APIs, including JDO, Hibernate and iBatis.
-
Spring Web
The Spring Web module is part of Spring?s web application development stack, which includes Spring MVC.
-
Spring DAO
The DAO (Data Access Object) support in Spring is primarily for standardizing the data access work using the technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO.
-
Spring Context
This package builds on the beans package to add support for message sources and for the Observer design pattern, and the ability for application objects to obtain resources using a consistent API.
-
Spring Web MVC
This is the Module which provides the MVC implementations for the web applications.
-
Spring Core
The Core package is the most import component of the Spring Framework.
This component provides the Dependency Injection features. The BeanFactory provides a factory pattern which separates the dependencies like initialization, creation and access of the objects from your actual program logic.
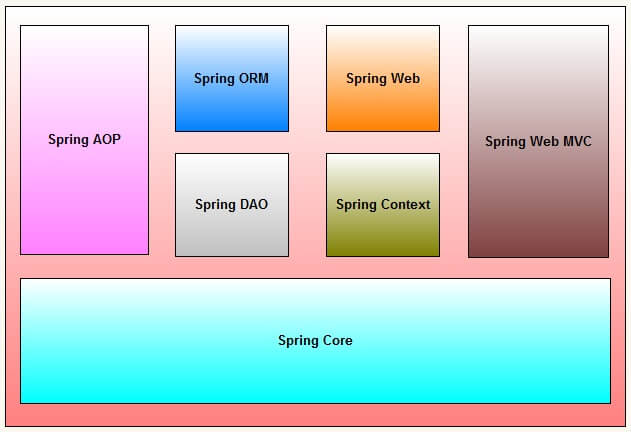 |
| Spring Framework Architecture |


