Table of Contents
Spring autowiring byType means autowiring on the basis of datatype. if any bean property datatype matches with exact one other bean’s datatype declaration then spring will automatically takes care of dependency. If more than one bean property matches, then it throws fatal exception.
Below diagram will make it clear:
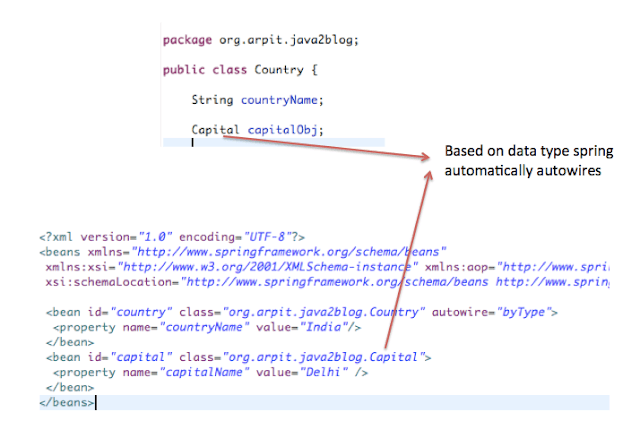
For example:
I am taking example of autowire “byType” here.It will be almost same as Dependency injection via setter method with some changes in XML configuration file.
1.Country.java:
This is simple pojo class having some attributes so here country has name and object of Capital class.
Create Country.java under package org.arpit.java2blog.Copy following content into Country.java.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class Country { String countryName; Capital capitalObj; public String getCountryName() { return countryName; } public void setCountryName(String countryName) { this.countryName = countryName; } public Capital getCapitalObj() { return capitalObj; } public void setCapitalObj(Capital capitalObj) { this.capitalObj = capitalObj; } } |
2.Capital.java
This is also simple pojo class having one attribute called “capitalName”.
Create Capital.java under package org.arpit.java2blog.java.Above Country class contains object of this class.Copy following content into Capital.java
Here in ,we have used autowire attribute and set it to “byType”.So now spring container will match Capital datatype in Country class with type of other beans in XML configuration file. So here you can see we have bean with class as Capital.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class Capital { String capitalName; public String getCapitalName() { return capitalName; } public void setCapitalName(String capitalName) { this.capitalName = capitalName; } } |
3.BeanAutowiringByTypeMain.java
This class contains main function.Create BeanAutowiringByTypeMain.java under package org.arpit.java2blog.Copy following content into BeanAutowiringByTypeMain.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class BeanAutowiringByTypeMain{ public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml"); Country countryObj = (Country) appContext.getBean("country"); String countryName=countryObj.getCountryName(); String capitalName=countryObj.getCapitalObj().getCapitalName(); System.out.println(capitalName+" is capital of "+countryName); } } |
You can note here that we have used ClassPathXmlApplicationContext for getting bean here.There are various ways for getting beans.In hello world example we have used XmlBeanFactory for getting beans.
4.ApplicationContext.xml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="country" class="org.arpit.java2blog.Country" autowire="byType"> <property name="countryName" value="India"/> </bean> <bean id="capital" class="org.arpit.java2blog.Capital"> <property name="capitalName" value="Delhi" /> </bean> </beans> |
5.Run it
When you will run above application,you will get following as output.
|
1 2 3 |
Delhi is capital of India |
What if two properties of class have same datatype:
Change ApplicationContext.xml as below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="country" class="org.arpit.java2blog.Country" autowire="byType"> <property name="countryName" value="India"/> </bean> <bean id="capital1" class="org.arpit.java2blog.Capital"> <property name="capitalName" value="Delhi1" /> </bean> <bean id="capital2" class="org.arpit.java2blog.Capital"> <property name="capitalName" value="Delhi2" /> </bean> </beans> |
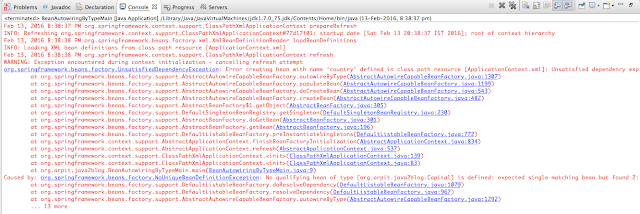
In above xml, we have declared two capital beans,now how it will autowire.
Answer: It won’t.
When you run above program, it will give you below exception:
It will give you below exception.
Was this post helpful?
Let us know if this post was helpful. Feedbacks are monitored on daily basis. Please do provide feedback as that\'s the only way to improve.


