Table of Contents
- What is an instruction set architecture?
- What exactly is a “bit”?
- x86 vs x64 – Features you need to know
- X86 vs X64 – A Quick Comparison
- What is the difference between x86 vs x64 bit?
- x86 vs x64 – What is the Future?
- ARM – The Portable Architecture
- ARM vs x86 and x64
- Pros and Cons of using ARM
- Pros and Cons of using x86 or x64
- FAQs
The comparison of x86 vs x64 in terms of CPU architecture isn’t exactly a new rivalry, but what really differentiates them? Here’s everything you need to know about the 32-bit and 64-bit architecture.
Computers and technologies have constantly been evolving with the day and age to meet the customer’s demands, and better, faster, and newer technologies are always appreciated. X86 and x64 are one such technology that has been a talk from the first-ever personal computers.
You must have heard these terms come across when you go shopping for a PC or a processor. But what is it, and how is it beneficial for you? We’ll be taking a comprehensive look at them and make a fair comparison of the technology.
What is an instruction set architecture?
An Instruction Set Architecture or ISA is an abstract model of computer architecture. It is mainly implemented in the CPU/Processor of the system and defines the supported data types, registers, main memory, and a lot more. You can sum it as the architecture that gives instructions to all the components and manage the entire operations of programs and apps. The primary examples of instruction set architecture are x86 and x64, generally termed 32-bit and 64-bit, respectively.
What exactly is a “bit”?
Now that we know what is an instruction set architecture and what bit sizes are they based on. Let us look at what a bit is. A single bit is the smallest unit of data in a computer, and it can either be a 0 or 1. It is used to represent information in a computer and can be grouped together to form usable data.
A grouping of 8 bits make up a byte, and a Kilobyte (KB) is 1024 bytes. You can then combine kilobytes to make up a Megabyte (MB) which is 1024 Kilobytes. Similarly, a Gigabyte (GB) is 1024 Megabytes, and a Terabyte (TB) is 1024 Gigabytes with more and more increments in data leading to Peta and zeta bytes of data.
x86 vs x64 – Features you need to know
Both the instruction set architectures have some primary standard features that help operate the computer system, and they are:
32-bit (x86) Features:
- It uses the Complex Instruction set computing Architecture (CISC)
- Execution of complex instructions is done with many cycles
- The hardware approach to performance is given more priority
- It has more registers and less memory
- Uses a software-based version of DEP
- It is designed with fewer pipelines and can handle complex addresses
- Can use only 4GB of memory space
64-bit (x64) Features:
- It has a larger virtual address space
- Huge files can be operated on by simultaneously processing on multiple address spaces
- It also has support for more RAM and memory space
- Instructions can be loaded more effectively and efficiently
- Supports hardware-backed DEP
- Has backward compatibility and can run 32-bit programs
X86 vs X64 – A Quick Comparison
| Instruction Set | x86 | x64 |
| Architecture | 32-bit | 64-bit |
| Registers, Memory and Data Bus | 32-bit memory and data bus, 32-bit registers | 64-bit memory and data bus, 64-bit registers |
| Maximum addressable memory | 2^32 bytes = 4GB | 2^64 bytes = 16 exabytes |
| Computation Power | Less powerful and slower as compared to x64 | Faster processing and can compute a more extensive set of integers |
| Value Storage | Uses more registers to split and store values | Can store larger values with fewer registers |
| Parallel Data Transmission | It can only transmit 32-bits of information | Can transmit larger 64-bit data along the larger data bus |
| Introduced on year | 1978 (by Intel) | 2000 (by AMD) |
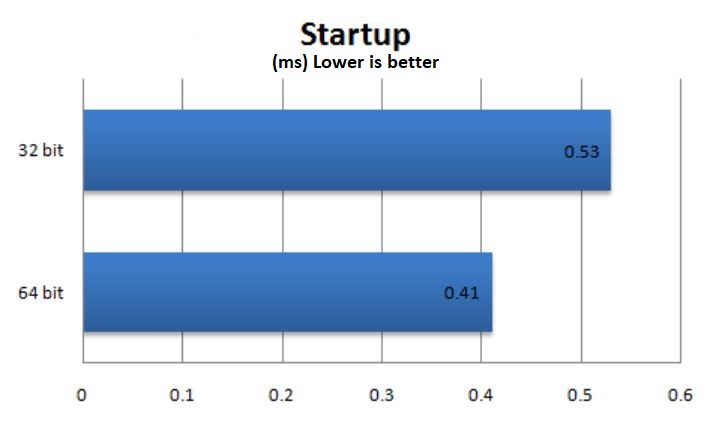
What is the difference between x86 vs x64 bit?
The x86 architecture was first introduced back in 1978 and ran on the Intel 8086 processor. It first had a 16-bit system which quickly got overthrown with newer instruction sets that used a 32-bit system which means that the processors have a 32-bit bus for memory and data and has 32-bit registers. However, the main difference is that x86 is limited to only 4GB of addressable memory space and can only parallel transmit 32-bits on a single go, making it slower than the 64-bit systems.
The x64 architecture is a recent architecture introduced back in the year 2000 as an extension for the 32-bit x86 architecture system. It was first seen with an AMD processor, which had a 64-bit bus for memory and data and had 64-bit registers. The 64-bit architecture has a lot more addressable memory and can reach a theoretical maximum of 16 exabytes or 16000 Petabytes of data. It can also transmit larger chunks of data along the 64-bit data bus and is inherently faster than the x86 architecture.
x86 vs x64 – What is the Future?
Now that we know what both architectures are comprised of and how they function or are different. Let us take a look at which architecture is read to bring innovations to the future.
Spoiler Alert: it’s not x86 (32-bit)
Windows and macOS
Windows and macOS are the two major operating systems that everyone uses. Linux is also very popular but is not primarily used by the common folk. All of these operating systems are capable of running both 32-bit vs 64-bit Operating Systems and is much more seamless with a 64-bit version. However, the most RAM that Windows and macOS can use with 64-bit architecture is 2TB and 128GB, respectively.
You can check which variant of the OS you are using by going to your respective OS Settings panel and looking for the device information section.
Portability (Android and iOS)
Android and iOS devices are the kings of portable operating systems, and both of these were first introduced with the x86 or 32-bit instruction set architectures. Android took the strides to move to 64-bit with their 5th iteration of Android, namely Android Lollipop (5.0), and iOS moved to a 64-bit model with iOS 11.
However, there are still 32-bit codes embedded into the OS as they need to be backwards compatible, but Apple claims to entirely move to the better 64-bit instruction set with future updates.
Browser Performance
The world is moving towards being a lot more connected with each other, and internet browsers are at the forefront of the movement. More and more apps are moving towards web and cloud servers for more effortless operation, and streaming services have become a lot more critical. In fact, game streaming is also on the rise, making it inevitable to become a mainstream platform. Hence, using an x86 vs x64 platform will just make it underperform and using it with the latest 64-bit platform will get you the best possible experience with all your favourite websites and web apps.
Audio
This is a weird section. You might think that 32-bit and 64-bit are data instruction sets. So, what does it have to do with audio? Well, audio is basically data and follows the 0 and 1 bits to store and play audio/music.
32-bit audio samples can store most of the information. They will sound perfect to your ears, but 64-bit audio comes into existence to be used with a lot of post-processing tools and plugins so that the overall data of the original sequence remains the same. However, 32-bit audio is much more common and preferred for easier access and compatibility reasons.
Memory and Performance
As discussed earlier 32-bit OS are slower and have a lower addressable memory size of just 4GB. This means that your OS can only take advantage of 4GB of RAM, making everything a lot slower from today’s standards.
This limitation was removed with the 64-bit extension, which supported faster processing and a lot more addressable memory. The theoretical maximum of RAM that you can use is 16000 Petabytes of data which is a lot more future proof and performance-optimized.
Limitations
The primary limitation for 32-bit Operating Systems, processors and architectures are:
- The limited pool of addressable memory
- The slower processing speeds
- Not-future ready
The primary limitations for 64-bit Operating Systems, processors and architectures are:
- It doesn’t natively run older legacy devices
X64 or X86 for Gaming
Gaming is a significant aspect of today’s day and age, and if you are looking for which architecture to base your game on, then follow the points below:
- Most older games run on 32-bit architecture
- 32-bit is better for emulation
- Backwards Compatibility and Legacy Support with 32-bit architecture set
- 64-bit is better for newer game engines
- x64 is faster and can allocate a lot more performance
In Short, x64 or 64-bit is better and quicker for more recent games and gaming engines, whereas 32-bit or x86 is better for emulation and older hardware.
TLDR; 64bit or x64 is the future as it has a lot more performance and is easily implemented with the newer processors and Operating Systems. However, 32-bit is better at older games and hardware for emulation.
ARM – The Portable Architecture
ARM is the new architecture that is making headlines with mobile devices. ARM or Advanced RISC Machines is a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture developed for computer processors. It is the most pervasive processor architecture, with billions of ARM-based devices shipped every year. The chips have various usages starting from sensors, wearables, and smartphones to even supercomputers and desktop machines.
All Android and Apple chips use it, and the underlying base was first released with a 32-bit x86 system that finally got bumped up to arm64, the successor and made with 64-bit underlying code. Using ARM beings some benefits, and they are:
- Integrated security and privacy tools
- High-performance optimization and energy efficiency
- A massive ecosystem of devices and global support
- Easy to integrate and much cheaper
ARM is also looking to be the next future architecture with an impressive underlying 64-bit base and a lot of performance. However, as of now, ARM is still being adapted from the consumers and the developers. So, seeing a massive jump in desktop performance from an ARM chipset is highly unlikely, making the x64 architecture the current king for desktop platforms.
ARM vs x86 and x64
The x86 and x64 have been around for decades, and modern technologies demanded a new refresh. This is where ARM jumped in. Where x86 and x64 use the CISC architecture, ARM uses the RISC architecture. However, both of them have the same underlying bit array, with 32-bit and 64-bit taking the lead. There are a few advantages and disadvantages with using ARM or the conventional x86 and x64 instruction sets, and we’ll be looking at all of them to make a fair comparison.
Pros and Cons of using ARM
Pros
- It is excellent for power-efficient devices
- Has a lot of support with the smartphone industry
- Is RISC based
- Has an excellent future prospect
- It is constantly evolving with changes in the underlying system
Cons
- It is relatively new, and developers are still figuring out the best way to integrate ARM
- It doesn’t have powerful chips for desktop
- Has compatibility issues with some desktop apps
Pros and Cons of using x86 or x64
Pros
- Has a well-established developer base
- It is very powerful and delivers excellent performance for desktop applications
- Uses the CISC based architecture
- Has affordable costs for processors
- Much more compatible with all the desktop applications
Cons
- Is generally power-hungry
- Not suitable for smartphones or embedded systems
In Short; The ARM chips are excellent smartphone processors that can be forward a new future of devices if appropriately adapted, but the widely used x86 or an x64 instruction set is still standing strong and is the only architecture present in computers ranging from your desktop PCs to a supercomputer.
FAQs
Why is 32-bit called X86?
X86 first came out with 16-bit processors and was introduced with Intel CPUs. The name came from the Intel 8086 CPU lineup, but with time, it was adopted with 32-bit architecture and is now commonly used or is resonant with the 32-bit instruction sets and processors.
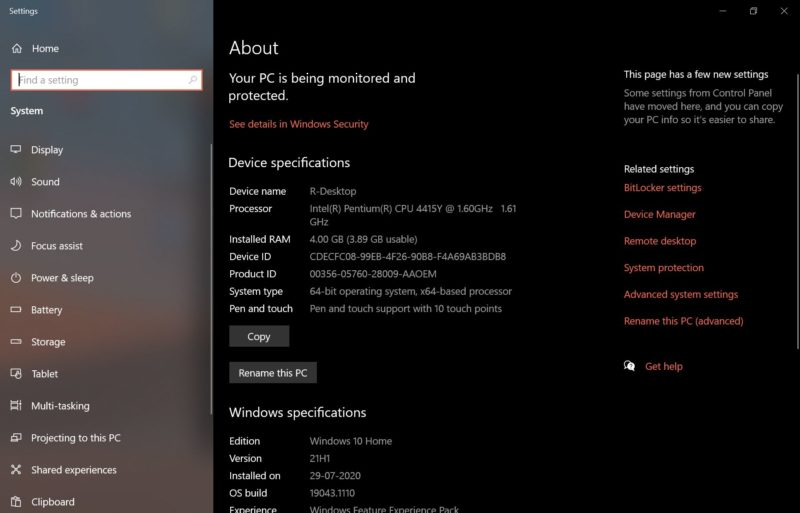
How do I find out if my computer is 32-bit or 64-bit?
You can find if your computer is 32-bit or 64-bit by going into the settings section and looking for device information. However, if you bought your computer in the past 10-15 years, rest assured as it most likely will be a 64-bit enabled system.
Here are the steps:windows key +X and click on the sysmtem.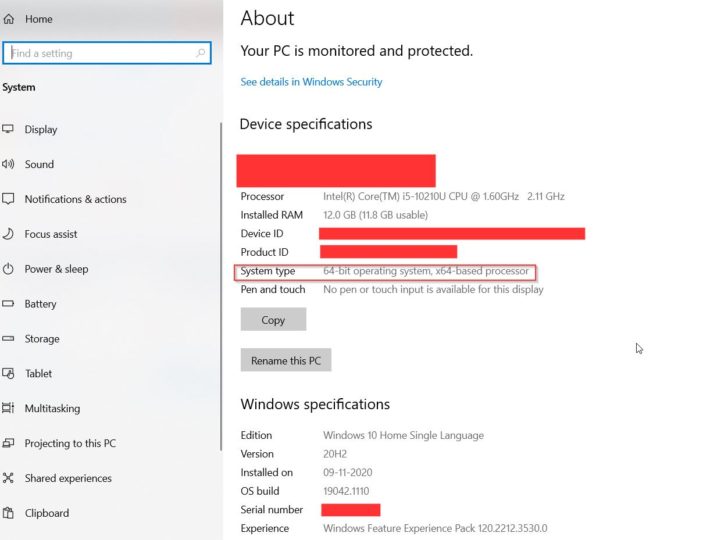
Is x64 faster than x86?
Yes, x64 is faster than x86 systems as they can allocate a lot more RAM and has parallel processing with a more significant 64-bit memory and data bus. It also has larger registers, and the overall performance with 64-bit OS and processors is a lot faster than 32-bit systems.
Can x86 run on x64?
Yes, x86 or 32-bit programs and apps can run on x64 or 64-bit architecture, but x64 can’t run on x86 instruction sets. x64 can emulate two x86 tasks at a single time and delivers a much faster and seamless experience.
Is my processor 64-bit or 32-bit?
If you have bought or are using a processor for the past 10-15 years, you likely have a 64-bit processor, and you can check this in your device information section or download an app like CPU-Z to get the most insight into your processor.