If you want to practice data structure and algorithm programs, you can go through 100+ Java coding interview questions.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
In this article, we will explore the concept of InOrder traversal in binary trees, focusing on its implementation in Java. In computer science, a binary tree is a foundational data structure, and traversing it is a fundamental technique. Among the various traversal methods, InOrder traversal is widely used due to its applications across a range of algorithms and operations.
2. What is InOrder Traversal?
3. Process of InOrder Traversal
- Traverse the
left subtreein InOrder. Visitthe node.- Traverse the
right subtreein InOrder.
4. Implementation
There can be two ways of implementing it
- Recursive
- Iterative
4.1 Recursive Solution
Recursive solution is very straight forward. Below diagram will make you understand recursion better.
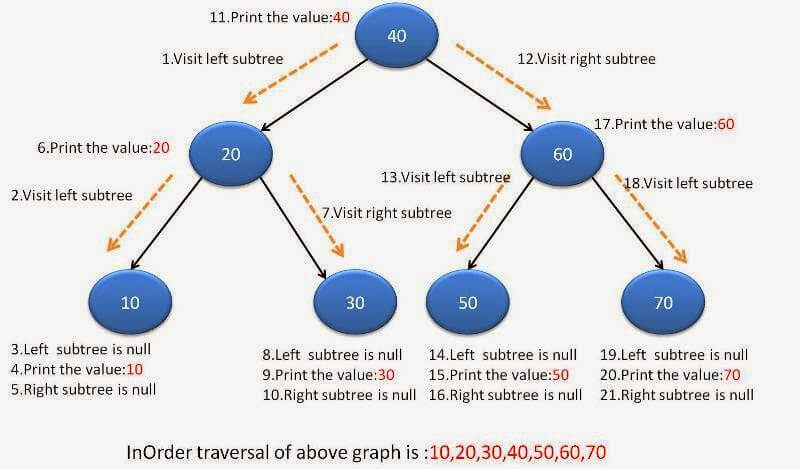
Code for recursion will be:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// Recursive Solution public void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root != null) { inOrder(root.left); //Visit the node by Printing the node data System.out.printf("%d ",root.data); inOrder(root.right); } } |
The time complexity for recursive approach is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. This is because each node in the tree is visited exactly once.
The space complexity is O(h), where h is the height of the tree. This complexity arises from the use of the call stack to handle recursion. In the worst case (a skewed tree), the height of the tree can become n, making the space complexity O(n).
4.2 Iterative Solution
For recursion, we use an implicit stack. To convert the recursive solution to an iterative one, we will use an explicit stack.
Steps for the iterative solution:
- Create an empty stack
sand initializecurrentNodeas root. - Push the
currentNodetosand setcurrentNode = currentNode.leftuntilcurrentNodeis null. - If
currentNodeis null andsis not empty, then:- Pop the top node from stack
sand print it. - Set
currentNode = currentNode.right. - Go to step 2.
- Pop the top node from stack
- If stack
sis empty andcurrentNodeis also null, then the traversal is complete.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// Iterative solution public void inOrderIter(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return; Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>(); TreeNode currentNode=root; while(!s.empty() || currentNode!=null){ if(currentNode!=null) { s.push(currentNode); currentNode=currentNode.left; } else { TreeNode n=s.pop(); System.out.printf("%d ",n.data); currentNode=n.right; } } } |
The space complexity is O(h), where h is the height of the tree. This complexity arises from the use of an explicit stack to keep track of nodes. In the worst case (a skewed tree), the height of the tree can become n, making the space complexity O(n).
5. Complete Java Program
Let’s say our binary tree is:
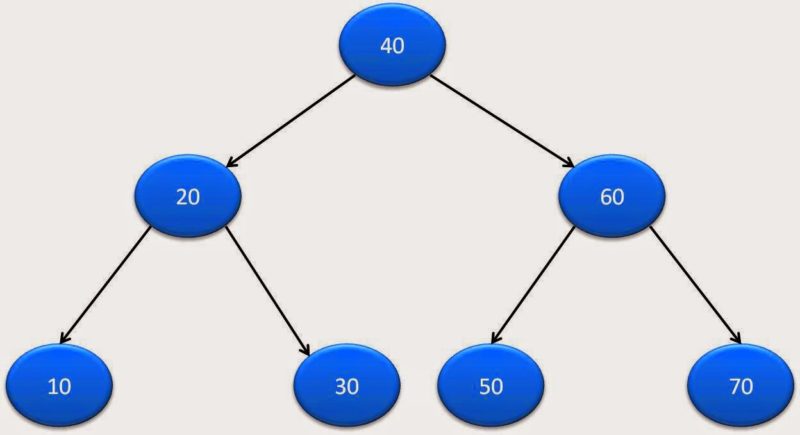
Here is complete java program for InOrder traversal:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.binarytree; import java.util.Stack; public class BinaryTreeInOrder { public static class TreeNode { int data; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int data) { this.data=data; } } // Recursive Solution public void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root != null) { inOrder(root.left); //Visit the node by Printing the node data System.out.printf("%d ",root.data); inOrder(root.right); } } // Iterative solution public void inOrderIter(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return; Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>(); TreeNode currentNode=root; while(!s.empty() || currentNode!=null){ if(currentNode!=null) { s.push(currentNode); currentNode=currentNode.left; } else { TreeNode n=s.pop(); System.out.printf("%d ",n.data); currentNode=n.right; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTreeInOrder bi=new BinaryTreeInOrder(); // Creating a binary tree TreeNode rootNode=createBinaryTree(); System.out.println("Using Recursive solution:"); bi.inOrder(rootNode); System.out.println(); System.out.println("-------------------------"); System.out.println("Using Iterative solution:"); bi.inOrderIter(rootNode); } public static TreeNode createBinaryTree() { TreeNode rootNode =new TreeNode(40); TreeNode node20=new TreeNode(20); TreeNode node10=new TreeNode(10); TreeNode node30=new TreeNode(30); TreeNode node60=new TreeNode(60); TreeNode node50=new TreeNode(50); TreeNode node70=new TreeNode(70); rootNode.left=node20; rootNode.right=node60; node20.left=node10; node20.right=node30; node60.left=node50; node60.right=node70; return rootNode; } } |
Run above program and you will get following output:
10 20 30 40 50 60 70
————————-
Using Iterative solution:
10 20 30 40 50 60 70
6. Conclusion
In this article, we covered about Binary tree InOrder traversal and its implementation. We have done traversal using two approaches: Iterative and Recursive. We also discussed about time and space complexity for the traversal.
Java Binary tree tutorial
- Binary tree in java
- Binary tree preorder traversal
- Binary tree postorder traversal
- Binary tree inorder traversal
- Binary tree level order traversal
- Binary tree spiral order traversal
- Binary tree reverse level order traversal
- Binary tree boundary traversal
- Print leaf nodes of binary tree
- Count leaf nodes in binary tree
- get maximum element in binary tree
- Print all paths from root to leaf in binary tree
- Print vertical sum of binary tree in java
- Get level of node in binary tree in java
- Lowest common ancestor(LCA) in binary tree in java


