Table of Contents
If you want to practice data structure and algorithm programs, you can go through Java coding interview questions.
In this post, we will see how to find Inorder Successor in a Binary Search Tree.
Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree and a target node value. Find the Inorder successor of the given node value in the Binary Search tree given. Inorder successor of any node ‘x’ is basically the node which gets traversed immediately after ‘x’ in the Inorder traversal of a tree.
Also assume that the node can not be the rightmost node of the given BST as no Inorder successor can exist for such node as this would be the last node to get traversed in the Inorder traversal.
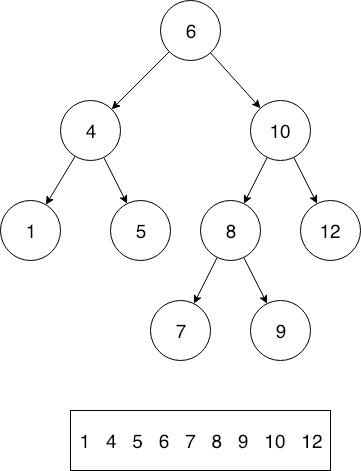
Inorder successor of 6 is 7 in this Binary Search Tree.
Solution
APPROACH – I :
A basic approach for finding inorder successor of any node in BST can be inspired by the fact that Inorder traversal of any Binary Search tree is sorted which means that Inorder successor of any node ‘x’ is the node having value greater than ‘x’ while being the smallest among all of these nodes having value greater than ‘x’
Let’s call this node as ‘next greater node’ which is actually the Inorder successor.
Now the problem boils down to finding this next greater node having value just greater than given target node.
So, for this, a simple preorder traversal would be enough, where at every node, we compare the node value with the target node and update our final answer if this current node has value greater than target node and lesser than final answer till now.
Time Complexity Discussion :
As we clearly need atleast a complete preorder or any traversal of the given Binary Search tree to explore all the nodes, hence, the worst time complexity of this approach for finding Inorder successor is O(n).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
package BinaryTrees; public class InorderSuccessor { public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } public String toString() { return data + ""; } } public static Node root; public static void main(String[] args) { root = new Node(6); root. left = new Node(4); root. right = new Node(10); root. left. left = new Node(1); root. left. right = new Node(5); root. right. right = new Node(12); root. right. left = new Node(8); root. right. left. left = new Node(7); root. right. left. right = new Node(9); /*for any rightmost node of a tree which is also the greatest * node in a tree, Inorder successor can not exist as it is * the very last node to get visited in the inorder */ System.out.println(getJustLarger(root, 9)); } public static int getJustLarger(Node node, int target) { /* return a maximum value in the basecase so that it * can not be able to update final answer to be returned */ if (node == null) return Integer.MAX_VALUE; /* result of recursive call to left subtree*/ int lr = getJustLarger(node.left, target); /* result of recursive call to left subtree*/ int rr = getJustLarger(node.right, target); /*final answer to be returned*/ int rv = Integer.MAX_VALUE; /* if the current node value is greater than target and * it is lesser than the greater values (greater than target * node value) explored till now, then update the final * answer to be returned*/ if (node.data > target && node.data < rv) { rv = node.data; } /* if the result of Left recursive call is greater than target and * it is lesser than the greater values explored till now, * then update the final answer to be returned*/ if (lr > target && lr < rv) { rv = lr; } /* if the result of Right recursive call is greater than target and * it is lesser than the greater values explored till now, * then update the final answer to be returned*/ if (rr > target && rr < rv) { rv = rr; } return rv; } |
Approach – II:
We know that Inorder successor of any element cannot lie in its left subtree as the Inorder successor of any node will definitely be greater than the target node and it is a property of binary search tree that no smaller value node can lie in the left subtree of any node.
Therefore, If a node has a right child, then its inorder successor should definitely be in the right subtree of that node.
Now, there can be two possibilities :
(i) If the target node has a right child :
As we know, inorder successor of any node is the next greater node in a Binary Search tree and next greater node of any node is the leftmost node in the right subtree of that node. In simpler terms, next greater node of any node ‘x’ must be the smallest node among all the nodes having value greater than ‘x’ and we know, right subtree in a Binary Search tree contains all the greater nodes. Now, smallest node among all these greater nodes will be leftmost node. Hence, If the target node has a right child then, its Inorder successor will be leftmost node in its right subtree.
(ii) If the target node does not have a right child :
Now, as there is no Right subtree belonging to the target node, therefore, now we need to find the next greater node in a traversal starting from root, but since we have a Binary search tree to work with hence we can find the next greater node efficiently.
How?
We always start the traversal from root node and compare the value of current node with the target node whose inorder successor has to be found and
- if it is greater than target node value, then update the final answer and move to the left subtree, WHY? because there is no benefit in going to right subtree as we will only find nodes with values greater than this current node, and as this node itself is greater than target node, this means it can be a potential
next greater nodebut nodes in its right subtree can certainly not. - if the current node is smaller than the target node, then move to the right subtree as we are looking for nodes having value greater than value of target node.
Time Complexity Discussion
Functions in both the cases (node with and without right child) traverse the tree in a linear path, that is, at every level we are either going to left subtree or the right subtree which makes the worst time complexity of this approach to O(height) and height of a tree is O(log n), where n is the number of nodes.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 |
package BinaryTrees; public class InorderSuccessor { public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } public String toString() { return data + ""; } } public static Node root; public static void main(String[] args) { root = new Node(6); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(10); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(8); root.right.left.left = new Node(7); root.right.left.right = new Node(9); /*for any rightmost node of a tree which is also the greatest * node in a tree, Inorder successor can not exist as it is * the very last node to get visited in the inorder*/ System.out.println(getInsucc(5)); } public static int getInsucc(int data) { /*find the object of the Node having data equal to given data */ Node node = find(root, data); /* if the right child of the node whose inorder successor * is to be found is not null, then it means its inorder * successor will lie in the right side only having actual * value equal to smallest node in its right subtree*/ if (node.right != null) { return rightsmallest(node).data; } else { /* if if the right child of the node whose inorder successor * is to be found is null, then we need to run an efficient * traversal starting from root looking for a value just greater * than given node */ nextGreaterEfficient(root, data); return inSuc.data; } } public static Node find(Node node, int data) { /*negative basecase : if node is null, return null*/ if (node == null) { return null; } /*positive basecase : node found*/ if (node.data == data) { return node; } /* result of recursive call to left subtree*/ Node lr = find(node.left, data); /* result of recursive call to left subtree*/ Node rr = find(node.right, data); /*if left subtree result and right subtree result, both * are null, this means, node does not lie in either of * the subtree of current node, and hence return null*/ if (lr == null && rr == null) { return null; /*if only one side is null. then node was found in * the other subtree and hence return the result of * ecursive call to that subtree*/ } else if (rr == null) { return lr; /*we have to have atleast one of either left result * or right result to be null, as a node can not be * present in both left and right subtree of any node*/ } else { return rr; } } public static Node rightsmallest(Node node) { /* firstly, shift the current node to right child of the * current node. This can never lead to a null pointer * exception as we call this function only when we ensure * that the node has a right child*/ Node curr = node.right; /* keep on shifting the current node to left, until we * find a node with no left child*/ while (curr.left != null) { curr = curr.left; } return curr; } public static Node inSuc = null; public static void nextGreaterEfficient(Node node, int target) { if(node==null) { return; } /* when we find a node having value greater than the target * node, then there is no point in going right side, * as we will only find nodes having value greater than this * node, therefore we update the final answer and move to left * subtree*/ if(node.data > target) { inSuc = node; nextGreaterEfficient(node.left, target); }else { nextGreaterEfficient(node.right, target); } } } |
When you run above program, you will get below output:
That’s all about Inorder Successor in a Binary Search Tree.


