Table of Contents
In this article, we will see how to implement stack in C++ using linked list.
Stack as an Abstract data Type
Stack is an ordered data structure to store datatypes in LIFO (Last In First Out) order. That means the element which enters last are first to exit(processed). It’s like a bunch of concentric rings kept one by one over others. Of course, the last one would be picked first when we start moving them out one by one (Tower of Hanoi). Stack is a similar data type where both insertion and deletion are done on the same side, namely top. Stack only hold similar datatypes.
The insertion process is named as Push
The deletion process is named as Pop
Operations on Stack
Type_t =any datatype
Basic operations:
Push(Type_t data): It inserts data of datatype Type_t to the stack
Type_t Pop(): Removes the topmost element from stack and returns it
Other operations:
Type_t top(): Returns topmost element
bool isEmpty(): returns true if stack is empty, else returns false
bool isFull(): returns false if stack is full, else returns false
int size(): Returns size of the stack
Stack Implementation using single linked list
A linked list is itself a data structure where every element has data and a pointer(next) to point the next element.
| data | next pointer |
Each node like the above is a stack element
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
class stackNode { //class for stack element which is SLL public: int data; //data stackNode *next; //next pointer stackNode(int a) { //constructor data = a; next = NULL; } }; |
Pre-requisites
- Single Linked List class/struct
- top pointer
Let’s check an example to understand push and pop implementation
Example:
Let the elements inserted are
1, 2, 3
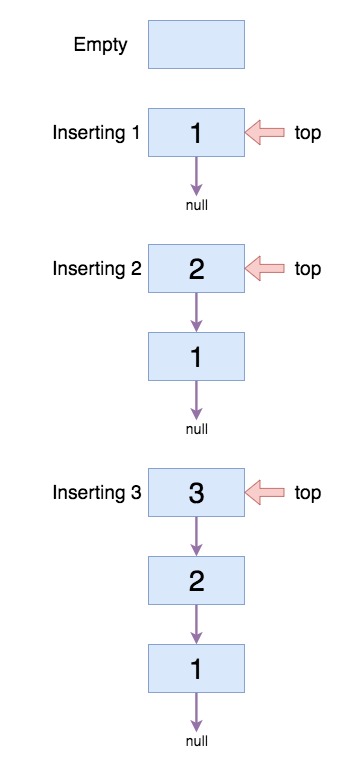
So to implement a stack with linked list,
When we push an element we actually do, inserting element at the head single linked list.
When we pop an element we actually do, deleting element from the head of single linked list.
C++ implementation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 |
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class stackNode { //class for each node which is a single stack element public: int data; stackNode *next; stackNode(int a) { //constructor data = a; next = NULL; } }; stackNode *top=NULL; //top of stack initialized to NULL int size=0;// size of stack initialized to 0 void push(int x) { //push operation stackNode* node=(stackNode*)(malloc(sizeof(stackNode))); node->data=x; node->next=top; top=node; cout<<x<<" is pushed\n"; size++; } bool isEmpty(){ //isEmpty function if(top==NULL && size==0) return true; else return false; } int pop() { //pop operation if(isEmpty()){ cout<<"stack is empty\n"; return INT_MIN; } else{ size--; int temp=top->data; stackNode* tempNode=top; top=top->next; free(tempNode); return temp; } } int top_stack(){ //top() operation if(isEmpty()){ cout<<"stack is empty\n"; return INT_MIN; } else{ return top->data; } } //main function int main(){ //menu for operations //press 1 for push (with data) //press 2 for pop() //press 3 for top() //press 4 for size() //press 0 to exit() cout<<"press 1 for push\n"; cout<<"press 2 for pop()\n"; cout<<"press 3 for top()\n"; cout<<"press 4 for size()\n"; cout<<"press 0 for exit\n"; int choice; cout<<"press your choice\n"; cin>>choice; while(choice){ if(choice==1){ int data; cout<<"Enter element\n"; cin>>data; push(data); } else if(choice==2){ int item=pop(); if(item==INT_MIN){} else cout<<"Popped element: "<<item<<endl; } else if(choice==3){ int item=top_stack(); if(item==INT_MIN){} else cout<<"Top element: "<<item<<endl; } else if(choice==4){ cout<<"Size is: "<<size<<endl; } else cout<<"Invalid number, try again!\n"; cout<<"press your choice\n"; cin>>choice; } cout<<"Exiting...\n"; return 0; } |
Output:
press 2 for pop()
press 3 for top()
press 4 for size()
press 0 for exit
press your choice
2
stack is empty
press your choice
1
Enter element
5
5 is pushed
press your choice
1
Enter element
7
7 is pushed
press your choice
2
Popped element: 7
press your choice
3
Top element: 5
press your choice
4
Size is: 1
press your choice
2
Popped element: 5
press your choice
2
stack is empty
press your choice
3
stack is empty
press your choice
4
Size is: 0
press your choice
1
Enter element
9
9 is pushed
press your choice
2
Popped element: 9
press your choice
5
Invalid number, try again!
press your choice
0
Exiting…
That’s all about Stack Implementation in C++ using Linked List