Table of Contents
If you want to practice data structure and algorithm programs, you can go through Java coding interview questions.
In this post, we will see how to find all subsets of set or power set in java.
Problem
Given a set of distinct integers, arr, return all possible subsets (the power set).
For example:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[] ]
We will use two approaches here.
Using recursion
You can find all subsets of set or power set using recursion. Here is the simple approach.
- As each recursion call will represent subset here, we will add resultList(see recursion code below) to the list of subsets in each call.
- Iterate over elements of a set.
- In each iteration
- Add elements to the list
- explore(recursion) and make start = i+1 to go through remaining elements of the array.
- Remove element from the list.
Here is java code for recursion.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class SubsetsOfSetJava { public static void main(String[] args) { SubsetsOfSetJava soa= new SubsetsOfSetJava(); int[] nums= {1, 2, 1}; List<List<Integer>> subsets = soa.subsets(nums); for (List<Integer> subset: subsets) { System.out.println(subset); } } public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); subsetsHelper(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, 0); return list; } private void subsetsHelper(List<List<Integer>> list , List<Integer> resultList, int [] nums, int start){ list.add(new ArrayList<>(resultList)); for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){ // add element resultList.add(nums[i]); // Explore subsetsHelper(list, resultList, nums, i + 1); // remove resultList.remove(resultList.size() - 1); } } } |
Output
Let’s understand with the help of a diagram.
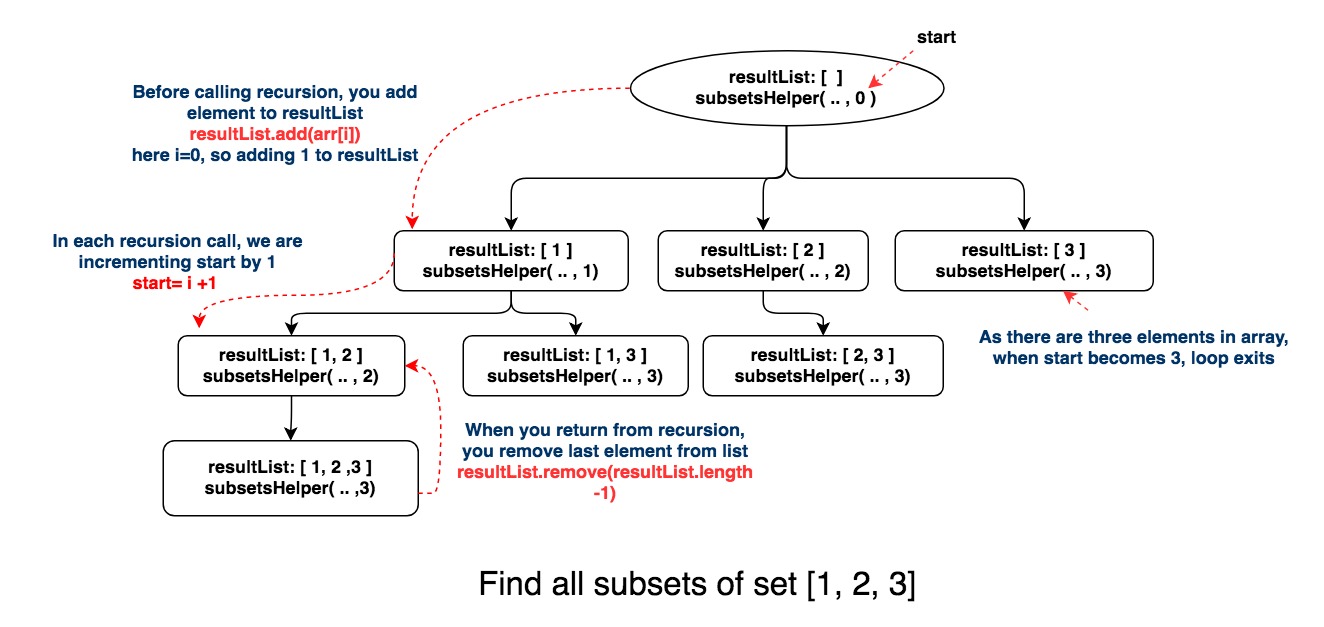
If you notice, each node(resultList) represent subset here.
Using bit manipulation
You can find all subsets of set or power set using iteration as well.
There will be 2^N subsets for a given set, where N is the number of elements in set.
For example, there will be 2^4 = 16 subsets for the set {1, 2, 3, 4}.
Each ‘1’ in the binary representation indicate an element in that position.
For example, the binary representation of number 6 is 0101 which in turn represents the subset {1, 3} of the set {1, 2, 3, 4}.
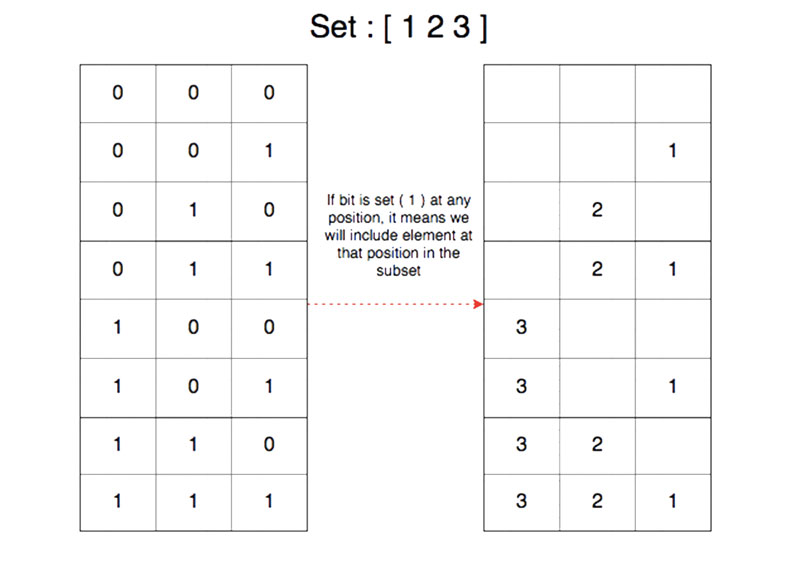
How can we find out which bit is set for binary representation, so that we can include the element in the subset?
To check if 0th bit is set, you can do logical & with 1
To check if 1st bit is set, you can do logical & with 2
To check if 2nd bit is set, you can do logical & with 2^2
.
.
To check if nth bit is set, you can do logical & with 2^n.
Let’s say with the help of example:
For a set {1 ,2, 3}
0 1 1 & 0 0 1 = 1 –> 1 will be included in subset
0 1 1 & 0 1 0 = 1 –> 2 will be included in subset
0 1 1 & 1 0 0 =0 –> 3 will not be included in subset.
Here is java code for the bit approach.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class SubsetBitMain { // Print all subsets of given set[] static void printSubsets(int set[]) { int n = set.length; // Run a loop from 0 to 2^n for (int i = 0; i < (1<<n); i++) { System.out.print("{ "); int m = 1; // m is used to check set bit in binary representation. // Print current subset for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if ((i & m) > 0) { System.out.print(set[j] + " "); } m = m << 1; } System.out.println("}"); } } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int set[] = {1 ,2, 3}; printSubsets(set); } } |
Output
{ 1 }
{ 2 }
{ 1 2 }
{ 3 }
{ 1 3 }
{ 2 3 }
{ 1 2 3 }
Here is complete representation of bit manipulation approach.
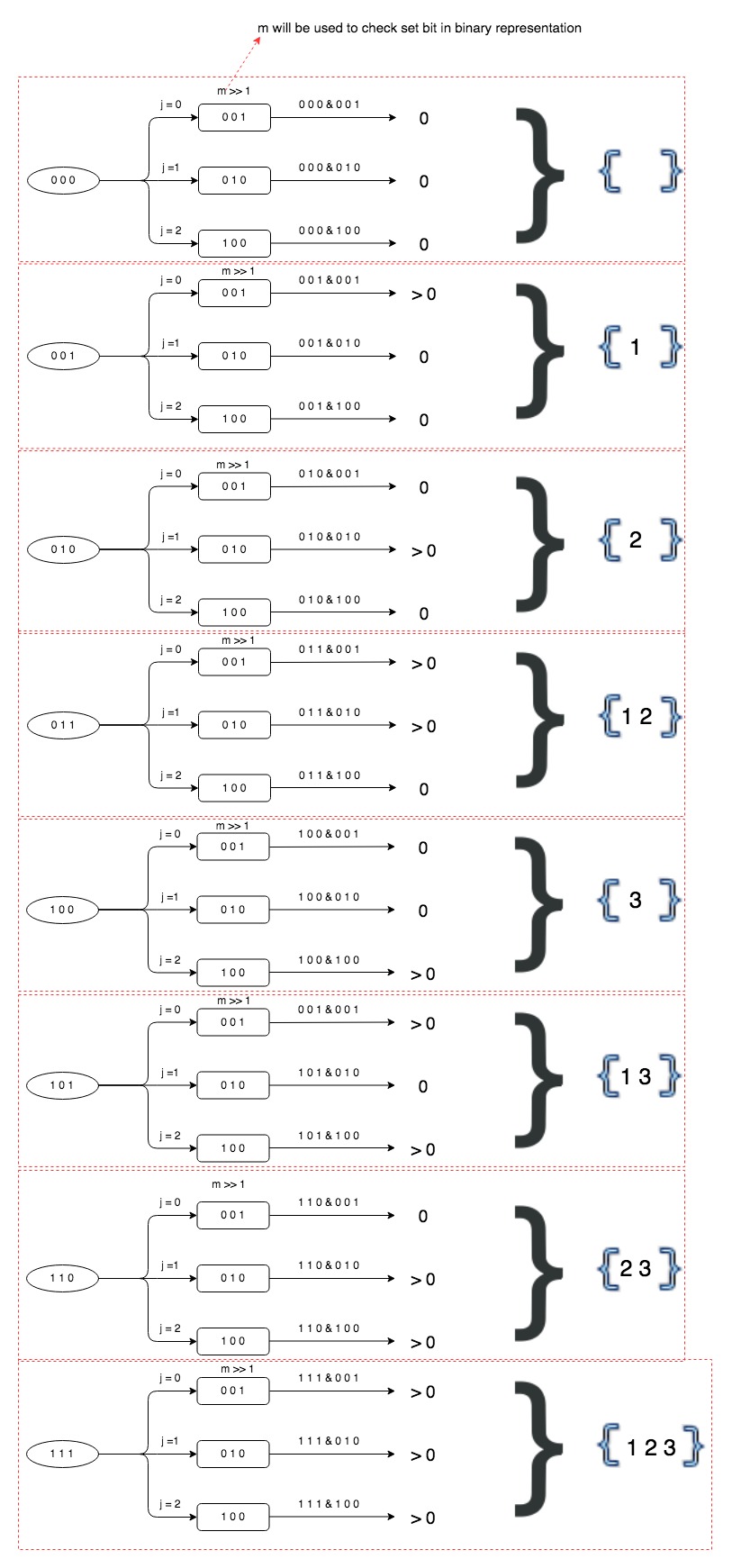
That’s all about finding all subsets of set(power set).
Hey,
Amazing job and a great explanation. Keep up the good work. You are helping the community. I completely support you.
Best explanation ever seen for recursion and subset. The tree diagram helped a lot ! Thanks!
Thank you for explanation. That makes bit manipulation algorithm much more comprehendable.