Table of Contents
Breath First Search is a graph traversal technique used in graph data structure. It goes through level-wise. Graph is tree like data structure. To avoid the visited nodes during the traversing of a graph, we use BFS.
In this algorithm, lets say we start with node x, then we will visit neighbours of x, then neighbours of neighbours of x and so on.
Algorithm
To traverse a graph using BFS, we use queue to store the nodes and array data structure to distinguish the unvisited nodes.
- 1. Create empty queue and push unvisited vertex to it.
- 2. Do following unless queue is empty.
- 2.1 pop the element from queue
- 2.2 Push unvisited adjacent nodes of the popped node into the queue.
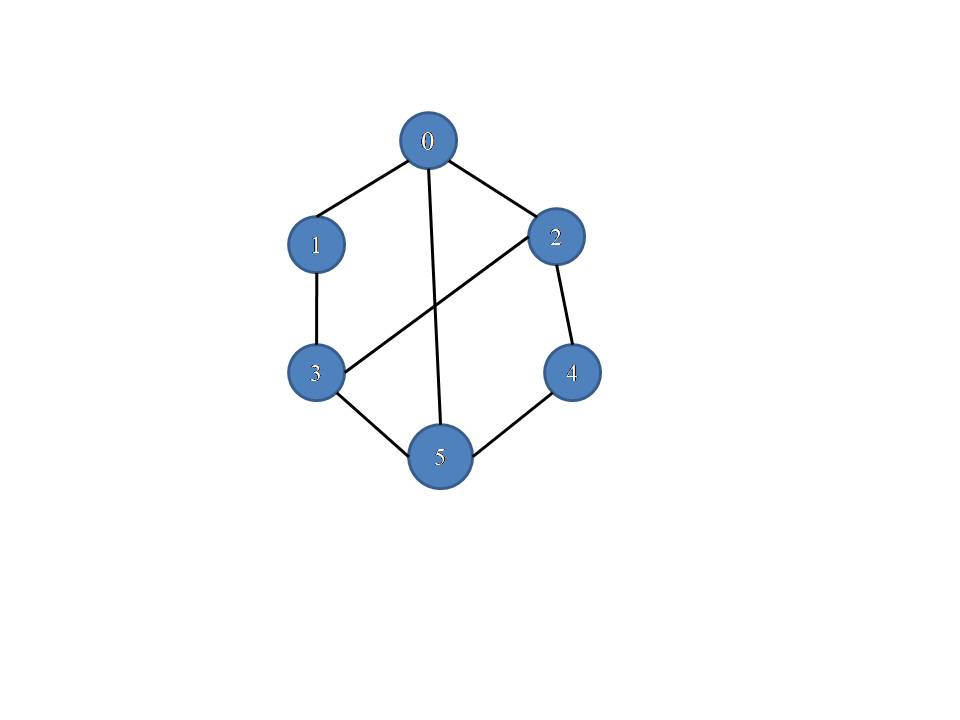
Consider this graph
According to our algorithm
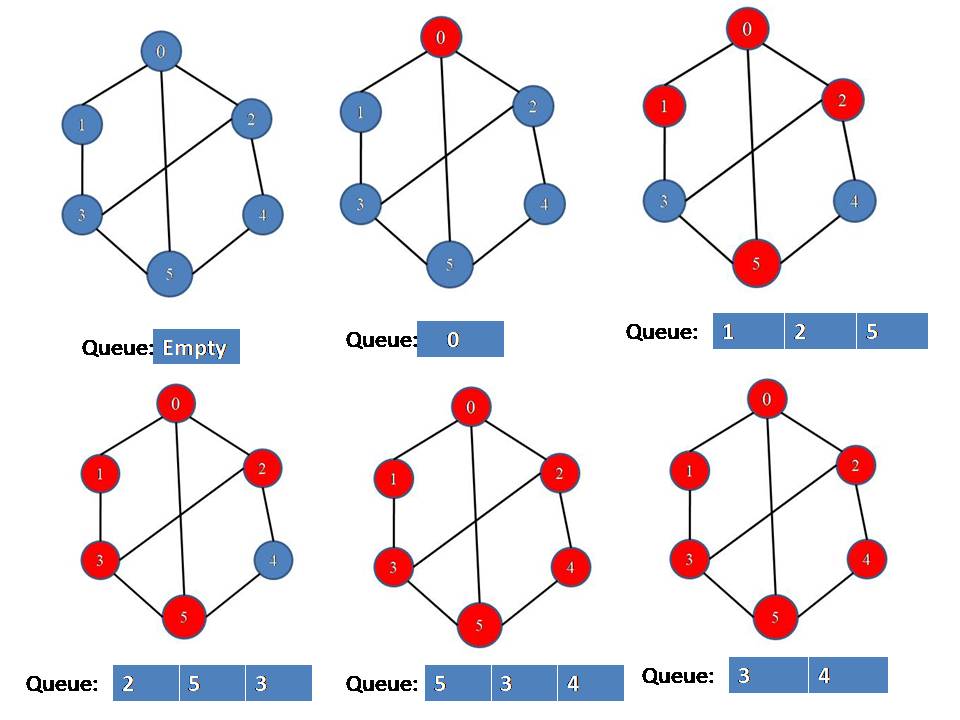
Hence all the vertices are visited, then the only pop operation is performed, and queue will be empty then.
Implementation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; void connect_edges(list<int>,int ,int ); void BFS(list<int>*,int); void connect_edges(list<int> *lst,int X,int Y){ //for the undirected graph we have to make a link of X-->Y and Y-->X lst[X].push_back(Y); lst[Y].push_back(X); return; } void BFS(list<int>*lst,int count,int X){ //created a boolean array to find out the unvisited nodes bool *visited= new bool[count]; for(int i=0;i<count;i++){ visited[i]=false; } queue<int> q; q.push(X); while(!q.empty()){ int ele=q.front(); q.pop(); //take one element from the queue and check the element is //unvisited or not if(!visited[ele]){ visited[ele]=true; //print the unvisited nodes cout<<ele<<" "; list<int>::iterator it; for(it=lst[ele].begin();it!=lst[ele].end();it++){ q.push(*it); } } } } // Print the Adjacency List void print(list<int> *lst,int count){ list<int>::iterator it; for(int i=0;i<count;i++){ cout<<i<<"-->"; for(it=lst[i].begin();it!=lst[i].end();it++){ cout<<*it<<"-->"; } cout<<endl; } } int main(){ int count; cout<<"Enter the no. of vertices : "; cin>>count; cout<<endl; list<int> *lst=new list<int>[count]; connect_edges(lst,0,1); connect_edges(lst,0,2); connect_edges(lst,2,4); connect_edges(lst,3,2); connect_edges(lst,4,5); connect_edges(lst,3,5); connect_edges(lst,1,3); connect_edges(lst,5,0); cout<<"Adjacency matrix: "<<endl; print(lst,count); cout<<"BFS : "<<endl; BFS(lst,count,0); return 0; } |
Output:
0–>1–>2–>5
1–>0–>3
2–>0–>4–>3
3–>2–>5–>1
4–>2–>5
5–>4–>3–>0
BFS :
0 1 2 5 3 4
That’s all about Breadth first search in C++.