Table of Contents
Introduction
In this post, we will look at Variables in Java Programming. It is an essential topic that will provide an insight into how a user stores and handles the data in the computer’s memory to use it efficiently.
So, we will cover everything from the definition to the declaration and the different types of variables in java.
What are variables in java?
In Java, variables are nothing but a named memory location. Variables in java stores values of elements while the program executes. All operations done on the variable affects the memory location.
Simply put, Variables are helpful to programmers to handle data that can be manipulated by the program during execution as well. Variables in java are Strongly typed; hence they all must have a datatype followed by an identifier.
Each variable has a specific Data Type that defines the size and layout of the variable’s memory.
How to Declare a Variable?
We can declare a variable as below:
|
1 2 3 |
data_type variable_name = value; |
Here is the example:
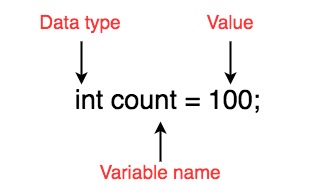
💡 Did you know?
Assigning value is optional while declaring variables. You can declare variable and assign value to it later in program.
Variable has a name that is used to identify it. The name of the variable is known as the variable’s identifier.
There are some naming conventions that you need to follow while declaring a variable.
- You can use
A to Zora to z. - You can use
0 to 9. - You can use special symbol
$and_to declare a variable. - You can not start a variable name with number.
- You can not have spaces in variable name.
- You can not use reserved keywords in variable name.
- Variables names are case sensitive.
Examples:
|
1 2 3 4 |
int age; String person_name; |
You can declare variables in groups as well like this:
|
1 2 3 4 |
int age,weight; String person_name,gender; |
How to Initialize Variables?
Each variable holds some data which it describes. We use = operator to assign value to a variable.
|
1 2 3 4 |
int age=30,weight=60; String person_name = "John"; |
Compiler will give compile time error if value does not match with the datatype of the variable.
For example:
You can not assign String literal to int data type.
|
1 2 3 4 |
// Compilation error int age= "NA" |
Let’s understand it with the help of simple program:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class VariableDemo { int a; // Instance variable static int b=20; // static variable public void print() { int c=10; // local variable System.out.println("Method local variable: "+c); } public static void main(String args[]) { VariableDemo demo=new VariableDemo(); System.out.println("Instance variable: "+demo.a); // Printing Instance variable System.out.println("Static variable: "+b); // Printing static variable demo.print(); //Printing local variable using print method. } } |
When you run above program, you will get the below Output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Instance variable: 0 Static variable: 20 Method local variable: 10 |
What are the different types of variables in java?
There are majorly three Types of Variables in use in Java Programming.
- Local Variable
- Instance Variable
- Static Variable
Let’s have a look at each type in detail with some examples.
Local variable
A variable declared inside a method or a block is termed a Local Variable. In Java, Local Variables can also be declared in a block within a method surrounded by curly braces; such variables are known as Block Level Local Variables.
In such a case, the scope of the variable, both in terms of its access and the presence of the variable in the memory, will be valid throughout the block only and not through the entire program. We will understand this with an example.
Note: It is mandatory to initialize the local variables; otherwise, the compiler will throw an error about it. Moreover, we cannot have Keywords like public, private, static associated with Local Variables.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
public class LocalVariablesDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { int x = 10; // Method Level Local Variable { int y = 20; // Block Level Local Variable System.out.println("Block Level Local Varibale y: "+y); } System.out.println("Method Level Local Variable x: "+x); } } |
Output:

Instance variable
A variable declared at the class level but outside a method or a block is an Instance variable. It is not mandatory to initialize instance variables. Instead, an Instance variable in Java is initialized when an instance of the class or an object is created.
All instance variables will be, by default, initialized by JVM. While allocating space for an object, a slot for each Instance Variable is also created. Thus, we can say Instance Variables are present in memory until the object’s lifetime and are visible to all methods and blocks in the class.
We can use Keywords and Access Modifiers with Instance Variables to restrict the visibility of the variables. Let us understand the use of instance variable with example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
public class InstanceDemo { int g; // Instance Variable with Default Value 0 public static void main(String args[]) { InstanceDemo obj=new InstanceDemo(); System.out.println("Instance variable g: "+obj.g); } } |
Output:
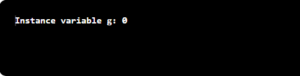
To access the value in the main method, we had to create the object or instance of the Class InstanceDemo; then, we used the dot operator with the object name to access the variable.
If we had accessed it directly without creating the object, the compiler would throw an error: non-static variable g cannot be referenced from a static context. This error means that the main method is static, and we cannot access a non-static variable from a static method. It is mandatory to instantiate the class in this case.
Static variable
A variable that is declared as static and refers to shared property for all class objects is known as a Static variable. Static variables are also class-level variables that can be declared in a method but only in a Static Method. We cannot declare static variables inside a Static Block.
Static Variables in Java make the program memory efficient as static variables get memory allocation only once during class loading. In simple words, all objects of a class will share the same static variable or properties.
Even if we create multiple objects or instances, static members are created only once. The static keyword denotes that a property belongs to the whole class rather than a method. Like Instance variables, Static members are also by default initialized by JVM. Let us understand the use of static variables with an example.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
public class StaticDemo { static int g; // Static Variable with Default Value 0 public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Static Variable g: "+g); //Accesing static variable of another class using Class Name System.out.println("Static Variable of Class Demo: "+ Demo.f); } } class Demo { static int f; // static variable in another class. } |
Output:

Here, we print the values of static variables of class: StaticDemo and Demo. Interesting thing we see that, there is no need to instantiate the class Demo to access its static variable we can access it just using the Class name and dot operator with the variable name.
Use Cases for different Variables in Java
Let’s assume we are trying to store information related to a Student object. Now, we know that each Student’s names and roll number are unique to them and are different, so we can use Instance Variables to store that kind of information.
Suppose we want to store information that will be the same for all Student Objects like their School Name, so in that case, we can use a Static variable so that every object shares the same variable. If we want to temporarily store any value related to the object for any operations, we can use Local Variables.
That’s all about Variables in Java Programming, you can try the above examples in your compiler to have a better understanding.


