Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Class In Java?
- How to Create a Class In Java : Example
- What is an Object In Java?
- How to Create an Object In Java : Example
- How to Create Multiple Objects for Same Class
- X Ways to initialize object in java
- Different ways to create an object in java
- Creating multiple objects by one type only
- Anonymous objects in Java
- What is the difference between Class and Object in Java?
Introduction
In this post, we will learn about Object and Class in Java. These topics form the core concepts and the building blocks of Object-Oriented Programming for a beginner.
As Java is an Object-Oriented Programming language, we design our program and represent/store key entities using Objects and classes.
What is Class In Java?
A class is a blueprint/template that defines the state and behavior of objects. It is the logical entity that wraps all our code into a single unit and structures the code. In Java, we cannot compile our code without a class. Hence, we must write the code only within the class body surrounded by Curly braces.
The unique characteristic of a class is that a user can define their data members (Variables with Data Types) and methods, and we can access them by creating instances of the class.
Declaration Syntax: In java, we declare the class following this syntax:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
class ClassName { // your code // fields // methods } |
How to Create a Class In Java : Example
Let us look at how a class looks like in a program.
Note: We can also declare a class with empty body i.e. with no data members and methods.
Let’s create a simple class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
public class Employee { String name; int age; public void workOnAssignment() { // Working on assignment } } |
Below given diagram explains the structure of class: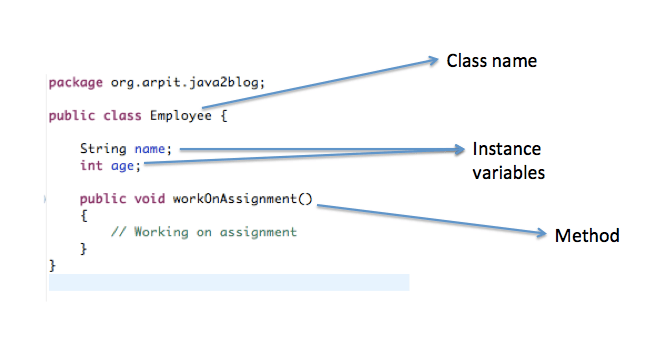
What is an Object In Java?
An entity that has a state and behavior is known as an Object. In java, an Object is an instance of a class. Objects are created during runtime based on the blueprint/template that a class provides.
It is crucial to create objects; without them, we cannot access our program’s class members and methods. An object typically has three characteristics:
- State: It represents the value of the Object.
- Behavior: It means the behavior (functionality) of an object.
- Identity: Java assigns a unique ID for each Object. The value of the ID is not visible to the external user.
Example: For the Employee class, each Employee object will have a state with name, age, and department, and behavior such as working on the assignment.
Declaration Syntax:
|
1 2 3 |
ClassName objectName = new ClassName(); |
How to Create an Object In Java : Example
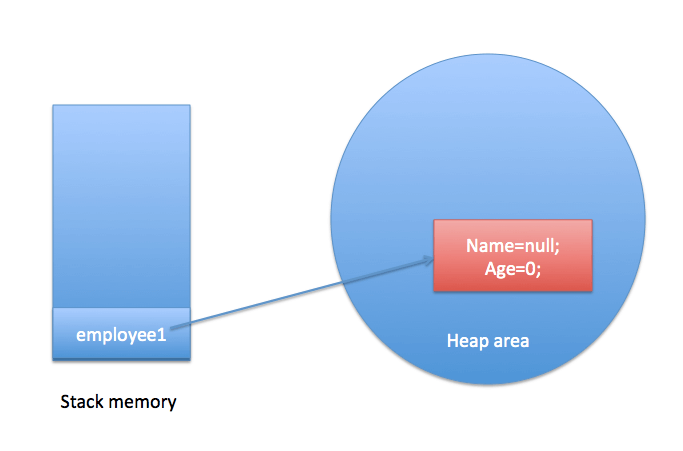
In Java, we use the new keyword to create an object to allocate memory dynamically as Objects are stored in heap memory. Now, let us create an object of the class Employee.
|
1 2 3 |
Employee employee1 = new Employee(); |
When above statement gets called, physical object is created in the memory as below:
How to Create Multiple Objects for Same Class
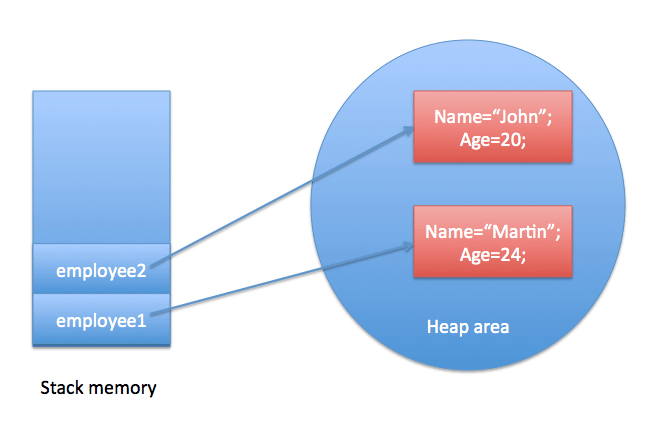
Now let’s create multiple objects for class Employee i.e. employee1 and employe2 and set the name and age for these two objects by accessing the members through object name.
Then we create the objects and set the values.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Employee employee1=new Employee(); employee1.name = "Martin"; employee1.age = 24; Employee employee2=new Employee(); employee2.name = "John"; employee2.age = 20; |
These two objects will be created in memory as below:
X Ways to initialize object in java
There are many ways to initialize objects in java. We will look at each in detail.
1. Using Object Name
We can initialize the object and assign value to the data members using the Object or Reference name and the dot operator as we did in the above example while creating multiple objects. Let us look at the whole program.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
class Employee { String name; int age; } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Employee employee1=new Employee(); // Initialize object values employee1.name = "Martin"; employee1.age = 24; // Print Values to check. System.out.println(employee1.name+" "+employee1.age); } } |
Output:

Note: We can access the members directly with Object name only if there are no Access Modifiers in the Employee class such as private.
2. Using Method
Instead of initializing the data members using object names, we can create a method inside the Employee Class that will assign values to the members of that object. We can pass the values while calling the method to initiate the object.
This is a convenient approach when using multiple objects because we don’t have to assign values using the object names individually.
Let us look at the example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
class Employee { String name; int age; void initialize(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } void display() { System.out.println(name+" "+age); } } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Employee employee1=new Employee(); Employee employee2=new Employee(); // Initialize object values employee1.initialize("Martin",25); employee2.initialize("John",23); // Calling display methods employee1.display(); employee2.display(); } } |
We call initialize method for each object we create and then display the values.
Output:

3. Using Constructors
We can initialize Objects using constructors, an internal feature provided by Java to instantiate objects.
4. Using Anonymous Inner Class Block
Another alternative to initialize an object is to use the “Double Brace Initialization”. This will create an anonymous inner class with an instance initializer in it. Inside we can call the initialize method and pass values. In this way, we need not call the methods explicitly with reference.
Let us look at the implementation.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
class Employee { String name; int age; void initialize(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } void display() { System.out.println(name+" "+age); } } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Employee employee1=new Employee(){ {initialize("Martin",23);} }; // Call display Method to check values. employee1.display(); } } |
Different ways to create an object in java
We can create objects in different ways apart from using the standard way by using the new keyword. There are 4 ways to create objects:
- Using newInstance() method of Class
- Using newInstance() method of Constructor Class.
- Using clone() method
- By Deserialization.
Creating multiple objects by one type only
We can create multiple objects of one reference or class type. We did the same for variables with primitive data types while declaring variables of same type in one line.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
int num1 = 10, num2 = 20; float g1 = 20, g2 = 30; |
Likewise, we can do the same for objects as well. We can create objects of Employee class same way. Instead of instantiating objects separately in two different lines we can write like this as well.
|
1 2 3 |
Employee emp1 = new Employee(); emp2 = new Employee(); |
This feature makes objects in Java closely related to variables when it comes to the declaration syntax and being programmer friendly.
Anonymous objects in Java
Anonymous objects are the objects which have no references. In simple words, these are objects with no names and can be used at the time of object creation only. We cannot reference the members of the class like ordinary objects, i.e., anytime.
Anonymous objects are the best option when the objects have to be used only once.
Example: So, if we have to create an anonymous object of class Employee, it would look like:
|
1 2 3 |
new Employee(); |
To call methods using Anonymous Objects we do this:
|
1 2 3 |
new ClassName().methodName(); |
Note: We cannot use Anonymous Objects to initialize member variables via methods. As no memory is allocated to such objects in the memory. However, we can instantiate the class using constructors with anonymous objects.
Now let us look at the program to use Anonymous objects and call methods from it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
class Employee { String name = "James"; int age = 24; // Constructor Employee() { } // Constructor with Parameters Employee(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } void initialize(String name,int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } void display() { System.out.println(name+" "+age); } } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { //using constructors to initialize name with given value and display it. new Employee("Maurice",22).display(); new Employee().display(); } } |
Output:

Here, we see without constructor we get the already initialized values. However, with Constructors we get the values with which we instantiate the objects.
What is the difference between Class and Object in Java?
Now, let us have a look at the key differences between Class and Object in java.
| Class | Object |
| 1. It is a blueprint or template for creating objects. | 1. It is an instance of a class which has a state and behavior. |
| 2. A Class characterizes a group of similar objects having same properties. | 2. An object represents a real world entity with some attributes and features. |
| 3. In java, Class is only loaded in memory during compile time for reference. | 3. On the other hand, Objects are allocated memory dynamically as they are created during runtime . |
| 4. A Class represents a logical entity which binds data and methods i.e. our code into a single unit. | 4. An Object is a physical entity which provides us means to access the members of a class. |
| 5. A Class is declared only once. We declare a class using keyword class. | 5. Objects can be created more than once depending on the requirement. We declare objects using new Keyword. |
| 6. We can define a class in only one way. | 6. Whereas, we can create objects in multiple ways like: Using newInstance() method, Using clone() method etc. |
So, that’s all about Object and class in java.


