Table of Contents
If you want to practice data structure and algorithm programs, you can go through 100+ java coding interview questions.
This is 9th part of java binary tree tutorial.
In this post, we will see about program to print all paths from root to leaf in a binary tree in java.
Below diagram will show all paths from root to leaf:
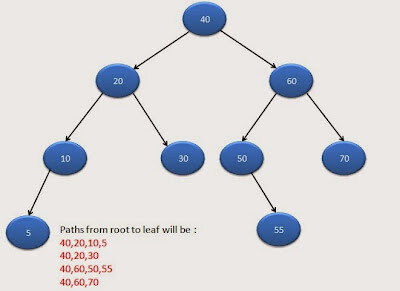
Algorithm:
Steps for print all paths from root to leaf are:
- If node is null then return 0
- put node.data in array and increment len by 1.
- If encounterd leaf node(i.e. node.left is null and node.right is null) then print array.
- Recursively visit left subtree and right subtree
Code for recursion will be:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// Prints all paths to leaf public static void printAllPathsToLeaf(TreeNode node, int[] path, int len) { if ( node == null ) return; // storing data in array path[len] = node.data; len++; if(node.left == null && node.right == null) { // leaf node is reached printArray(path,len); return; } printAllPathsToLeaf(node.left, path, len); printAllPathsToLeaf(node.right, path, len); } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.binarytree; public class BinaryTreePrintAllPaths { public static class TreeNode { int data; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int data) { this.data=data; } } // Prints all paths to leaf public static void printAllPathsToLeaf(TreeNode node, int[] path, int len) { if ( node == null ) return; // storing data in array path[len] = node.data; len++; if(node.left == null && node.right == null) { // leaf node is reached printArray(path,len); return; } printAllPathsToLeaf(node.left, path, len); printAllPathsToLeaf(node.right, path, len); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a binary tree TreeNode rootNode=createBinaryTree(); System.out.println("Printing all paths from root to leaf :"); printAllPathsToLeaf(rootNode,new int[1000],0); } public static void printArray(int[] path,int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(" "+path[i]); } System.out.println(); } public static TreeNode createBinaryTree() { TreeNode rootNode =new TreeNode(40); TreeNode node20=new TreeNode(20); TreeNode node10=new TreeNode(10); TreeNode node30=new TreeNode(30); TreeNode node60=new TreeNode(60); TreeNode node50=new TreeNode(50); TreeNode node70=new TreeNode(70); TreeNode node5=new TreeNode(5); TreeNode node55=new TreeNode(55); rootNode.left=node20; rootNode.right=node60; node20.left=node10; node20.right=node30; node60.left=node50; node60.right=node70; node10.left=node5; node50.right=node55; return rootNode; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Printing all paths from root to leaf : 40 20 10 5 40 20 30 40 60 50 55 40 60 70 |
Java Binary tree tutorial:
- Binary tree in java
- Binary tree preorder traversal
- Binary tree postorder traversal
- Binary tree inorder traversal
- Binary tree level order traversal
- Binary tree spiral order traversal
- Binary tree reverse level order traversal
- Binary tree boundary traversal
- Print leaf nodes of binary tree
- Count leaf nodes in binary tree
- get maximum element in binary tree
- Print all paths from root to leaf in binary tree
- Print vertical sum of binary tree in java
- Get level of node in binary tree in java
- Lowest common ancestor(LCA) in binary tree in java
Please go through java interview programs for more such programs.
Was this post helpful?
Let us know if this post was helpful. Feedbacks are monitored on daily basis. Please do provide feedback as that\'s the only way to improve.



I appreciate your blog. Its really nice on java programming. Its a great tutorial for the beginners. Really liked it. Thank you for all the information.
hi
can u plz help me
actually this following part of your code is not working, giving an error
plz resolve this
•if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
• // leaf node is reached
• printArray(path,len);
• return;
• }
•
thanks
Read more at https://www.java2blog.com/2014/08/print-all-paths-…
Thanks Tanu for pointing out. I have updated the code