If you want to practice data structure and algorithm programs, you can go through Java coding interview questions.
In this post, we will see how to find all permutations of the array in java.
Problem 1
Given array of distinct integers, print all permutations of the array.
For example:
array : [10, 20, 30]
Permuations are :
[10, 20, 30] [10, 30, 20] [20, 10, 30] [20, 30, 10] [30, 10, 20] [30, 20, 10]Solution
We can solve the problem with the help of recursion. It is quite hard to explain recursion, so I have created a recursion tree to demonstrate it.
Here is the code for the same.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class PermutateArray { public static void main(String[] args) { PermutateArray pa=new PermutateArray(); int[] arr= {10, 20, 30}; List<List<Integer>> permute = pa.permute(arr); System.out.println("Permuations of array : [10, 20, 30] are:"); System.out.println("========================================="); for(List<Integer> perm:permute) { System.out.println(perm); } } public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] arr) { List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); permuteHelper(list, new ArrayList<>(), arr); return list; } private void permuteHelper(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> resultList, int [] arr){ // Base case if(resultList.size() == arr.length){ list.add(new ArrayList<>(resultList)); } else{ for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ if(resultList.contains(arr[i])) { // If element already exists in the list then skip continue; } // Choose element resultList.add(arr[i]); // Explore permuteHelper(list, resultList, arr); // Unchoose element resultList.remove(resultList.size() - 1); } } } } |
When you run above program, you will get below output:
=========================================
[10, 20, 30] [10, 30, 20] [20, 10, 30] [20, 30, 10] [30, 10, 20] [30, 20, 10]
I have illustrated how recursion is working here with below diagram.
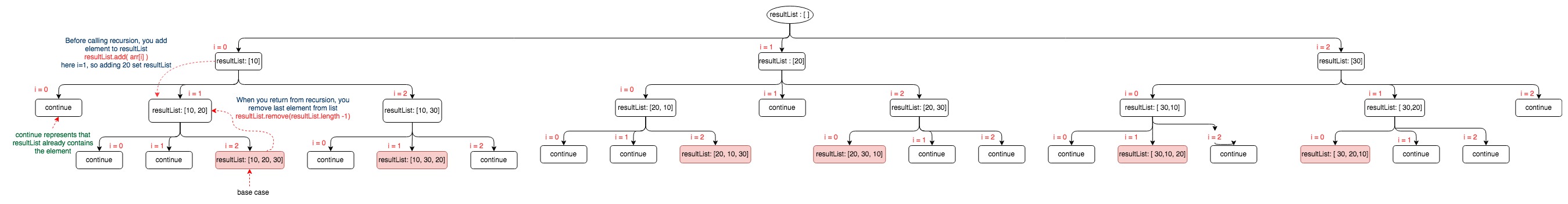
You need to open this diagram in new window and zoom it.
As we have 3 elements in the array, that’s why we have 3 branches for each node.
Problem 2
Given array of integers(can contain duplicates), print all permutations of the array.
Solution
We can solve this using recursion as well but need to take care of duplicates.We will sort the array, so all duplicates will be conitguous.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class PermuteArrayWithDuplicates { public static void main(String[] args) { PermuteArrayWithDuplicates pa=new PermuteArrayWithDuplicates(); int[] arr= {10, 20, 10}; List<List<Integer>> permute = pa.permute(arr); System.out.println("Permuations of array : [10, 20, 10] are:"); System.out.println("========================================="); for(List<Integer> perm:permute) { System.out.println(perm); } } public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] arr) { List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(arr); permuteHelper(list, new ArrayList<>(), arr,new boolean[arr.length]); return list; } private void permuteHelper(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> resultList, int [] arr, boolean [] used){ // Base case if(resultList.size() == arr.length){ list.add(new ArrayList<>(resultList)); } else{ for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ if(used[i] || i > 0 && arr[i] == arr[i-1] && !used[i - 1]) { // If element is already used continue; } // choose element used[i] = true; resultList.add(arr[i]); // Explore permuteHelper(list, resultList, arr, used); // Unchoose element used[i] = false; resultList.remove(resultList.size() - 1); } } } } |
=========================================
[10, 10, 20] [10, 20, 10] [20, 10, 10]
That’s all about Permutations of array in java.