Table of Contents
Logging is essential part of programming. It helps developer to track code workflow and fix bugs efficiently. If we get any issue in the code, we check logs for that workflow or functionality.
Log4j is fast , reliable logging framework and can be easily integrated with the code. It is possible to enable logging at run time without using
Lets integrate Log4j in simple maven project.
Steps:
1) Create simple maven java project.
2) Put log4j entry in pom.xml .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> |
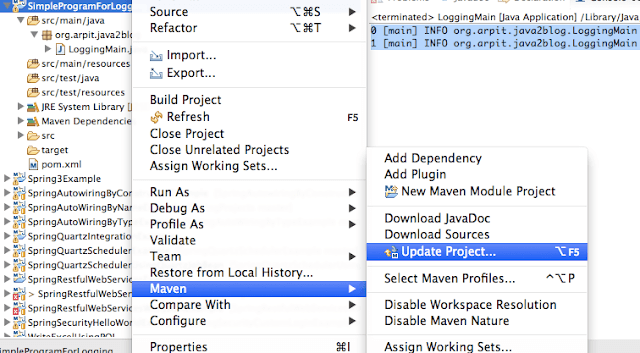
3) Update maven project to download require jar
Right click on project-> Maven -> update project

4) Sample class for Logger
Create a class called “LoggingMain.java” in src/main/java in package org.arpit.java2blog
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator; import org.apache.log4j.LogManager; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; public class LoggingMain { private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(LoggingMain.class); public static void main(String[] args) { // basic log4j configurator BasicConfigurator.configure(); logger.info("Hello world"); logger.info("we are in logger info mode"); } } |
5) Run program:
When you run above program , you will get below output:
|
1 2 3 4 |
0 [main] INFO org.arpit.java2blog.LoggingMain - Hellow world 1 [main] INFO org.arpit.java2blog.LoggingMain - we are in logger info mode |
Bingo!! we have successfully configured log4j in maven project.
Was this post helpful?
Let us know if this post was helpful. Feedbacks are monitored on daily basis. Please do provide feedback as that\'s the only way to improve.