Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Have you ever encountered a situation where you created an interface and several classes implemented it? Now, suppose you need to add new methods to the interface. Doing so would lead to a multitude of compilation errors across your Java project because you would need to incorporate these new methods into all classes that implement the interface. This is because if a class implements an interface, it must implement all of its methods.
Let’s take an example:
Create an interface called Decorable:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
public interface Decorable { void decorateWithCurtains(); } |
Now Create a class called Room which will implement this interface.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
public class Room implements Decorable{ public void decorateWithCurtains() { System.out.println("Decorate room with Curtains"); } } |
Now, this was your current implementation, and you have devised a new way of decorating that you wish to incorporate into the Decorable interface.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public interface Decorable { void decorateWithCurtains(); void decorateWithPaints(); } |
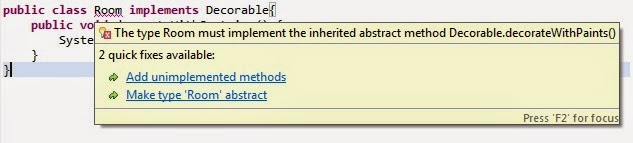
When you add decorateWithPaints() method to the Decorable interface, you will get following error in Room class:
2. What if We Use Default Method
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
public interface Decorable { void decorateWithCurtains(); default void decorateWithPaints() { System.out.println("Decorate using paints"); } } |
decorateWithPaints() a default method, so we will not encounter any errors in the Room class because we have provided a default implementation in the Decorable interface.
3. Why Default Methods
The one-liner for this could be “backward compatibility.” If the JDK modifies an interface, then all classes implementing this interface will break.
To introduce lambda expressions in Java 8, the JDK needed to add methods (such as forEach) to the List or Collections interface. However, adding this method to these interfaces would break millions of lines of code, as classes implementing the interface would need to implement all its methods.
By adding a default method to an interface, you can provide a default implementation without affecting the implementing classes, as it includes the method’s implementation. Any implementing class that needs to use this method can override it.
4. What About Multiple Inheritance?
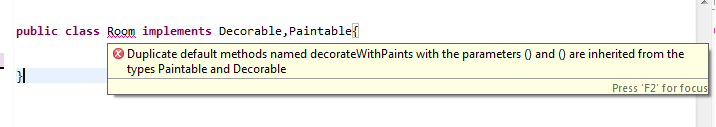
Adding a default implementation to an interface can lead to ambiguity in the case of multiple inheritance, as two interfaces can provide the same default method, resulting in ambiguity during invocation. Java 8 will generate a compile-time exception when this kind of situation arises.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
public interface Decorable { default void decorateWithPaints() { System.out.println("Decorate using paints"); } } public interface Paintable { default void decorateWithPaints() { System.out.println("Decorate using paints"); } } public class Room implements Decorable,Paintable{ } |
so it will give you compile time error as below:
You can solve this compilation error by overriding decorateWithPaints() method in Room class.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
public class Room implements Decorable,Paintable{ public void decorateWithPaints() { System.out.println("Decorate using paints"); } } |
5. Difference Between Default Methods and Abstract Class
Introduction of default methods to interface bridge gap between [interface](https://java2blog.com/interface-in-java-with-example/ “interface”) and [abstract class](https://java2blog.com/abstract-class-java/ “abstract class”).Now interface looks very similar to abstract classes but there are still differences. Lets list them
|
Parameter
|
Abstract class
|
Interface with default methods
|
|
State of objects
|
Abstract class can hold state of object
|
Interface with default methods can not hold state of objects
|
|
Access Modifier
|
Abstract class methods can have public ,protected,private and default modifier |
Interface methods are by default public. you can not use any other access modifier with it
|
|
Abstract class can have constructor
|
Interface can not have constructor
|
|
|
Member variables
|
It can have member variables
|