Table of Contents
Java Apache POI tutorial:
- Read excel files in java using POI
- Write excel files in java using POI
- Working with formula in excel using POI
- How to set style in excel using POI
In this post, we will see how to set and evaluate formulas in excel using Apache POI.
Set formula for a cell:
For setting a formula for cell, you need to use following code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// Setting cell formula and cell type Cell cell = row.createCell(2); cell.setCellFormula("SUM(C2:C5)"); cell.setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA); |
We will use same code which we have used to write CountriesDetails.xlsx in previous post and add row for total population and evaluate it using formula.
Java program:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook; public class WriteExcelMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { writeFileUsingPOI(); } public static void writeFileUsingPOI() throws IOException { //create blank workbook XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); //Create a blank sheet XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Country"); ArrayList<Object[]> data=new ArrayList<Object[]>(); data.add(new String[]{"Country","Capital","Population"}); data.add(new Object[]{"India","Delhi",10000}); data.add(new Object[]{"France","Paris",40000}); data.add(new Object[]{"Germany","Berlin",20000}); data.add(new Object[]{"England","London",30000}); //Iterate over data and write to sheet int rownum = 0; for (Object[] countries : data) { Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++); int cellnum = 0; for (Object obj : countries) { Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++); if(obj instanceof String) cell.setCellValue((String)obj); else if(obj instanceof Double) cell.setCellValue((Double)obj); else if(obj instanceof Integer) cell.setCellValue((Integer)obj); } } Row rowGap = sheet.createRow(rownum++); Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++); Cell cellTotal = row.createCell(0); cellTotal.setCellValue("Total Population"); // Setting cell formula and cell type Cell cell = row.createCell(2); cell.setCellFormula("SUM(C2:C5)"); cell.setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA); try { //Write the workbook to the file system FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("CountriesDetails.xlsx")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("CountriesDetails.xlsx has been created successfully"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { workbook.close(); } } } |
|
1 2 3 |
CountriesDetails.xlsx has been created successfully |
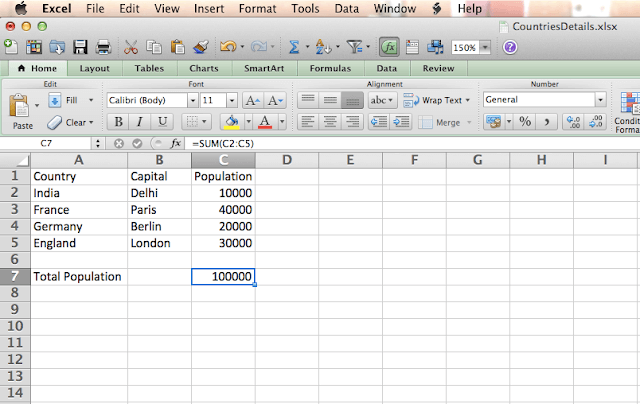
We have calculated total population using sum(c2:c5) in c7.
Formula evaluators:
When you update any cell which has impact on formula, you need to reevaluate the cell.
Apache poi API has provided FormulaEvalutor class to evaluate formula.
It has four method to evaluate formula:
1) public void evaluateAll()
It evaluates all cell which presents in workbook and it recalculates all formula and save the result and formula cells remains formula cells too. If cell do not have formula, it remains the same.
2) CellValue evaluate()
It evaluates formula cell and returns its cell value, it does not change original content of cell.
3) int evaluateFormulaCell(Cell cell)
It evaluates formula cell and returns its cell type. It saves calculated value. Cell remains as formula cell.
4) Cell evaluateInCell(Cell cell)
It evaluates formulas and return Cell object . It updates formula cell with latest value and cell will no longer formula cell.
Example for evaluate method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellValue; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.FormulaEvaluator; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook; public class ReadWriteExcelMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { readFileUsingPOI(); } public static void readFileUsingPOI() throws IOException { ClassLoader classLoader = ReadWriteExcelMain.class.getClassLoader(); String excelFilePath = "CountriesDetails.xlsx"; FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(classLoader.getResource(excelFilePath).getFile())); Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream); Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); // Creating formula evaluator object FormulaEvaluator formulaEval = workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator(); Iterator iterator = sheet.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Row nextRow = iterator.next(); Iterator cellIterator = nextRow.cellIterator(); while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue()); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue()); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue()); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA: { // Evaluting cell CellValue c=formulaEval.evaluate(cell); System.out.println(c.getNumberValue()); } } System.out.print(" | "); } System.out.println(); } workbook.close(); inputStream.close(); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
Country | Capital | Population | India | Delhi | 10000.0 | France | Paris | 40000.0 | Germany | Berlin | 20000.0 | England | London | 30000.0 | Total Population | 100000.0 | |


