Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Java 8 has introduced a new feature called Lambda expressions. This is considered to be major change for Java because it introduces a way of programming that is more about actions than the details of how things are done. Other languages such as
Scala already have this feature so this is not new to programming world, it is new to Java.In this article, we’re going to start from the basics and make it easy to understand what Lambda expressions are and why they are useful. Let’s begin by explaining what Functional Interfaces are, as they are key to understanding Lambda expressions.
2. What is Functional Interface?
Functional interfaces are those interfaces that have only one abstract method in it. It can have more than one default or static method and can override the method from
java.lang.object. Let’s create a functional interface:|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
@FunctionalInterface public interface Decorable { // one abstract method void decorateWithCurtains(); // default method default void decorateWithPaints() { System.out.println("Decorating using paints"); } // Overriding method of java.lang.Object @Override public int hashCode(); } |
Java can itself identify Functional Interface but we can also denote interface as Functional Interface by annotating it with
@FunctionalInterface.Some popular Functional Interfaces are:
- java.lang.Runnable
- java.util.concurrent.Callable
- java.awt.event.ActionListener
- java.util.Comparator
3. Why Lambda Expressions?
Let’s understand with help of Anonymous Comparator.
Let’s say we need to sort list of movies by movie name:
Movie.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class Movie { String movieName; long duration; public Movie(String movieName, long duration) { super(); this.movieName = movieName; this.duration = duration; } // getters and setters } |
Code to sort list of movies by name using comparator
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
Movie m1=new Movie("Inception",110); Movie m2=new Movie("GodFather",200); Movie m3=new Movie("Forest Gump",130); Movie m4=new Movie("Avengers",150); List<Movie> listOfMovies = new ArrayList<>(); listOfMovies.add(m1); listOfMovies.add(m2); listOfMovies.add(m3); listOfMovies.add(m4); System.out.println("Before Sort by name : "); for (int i = 0; i < listOfMovies.size(); i++) { Movie movie = (Movie) listOfMovies.get(i); System.out.println(movie); } // Sort by movieName // Anonymous Comparator // old way Collections.sort(listOfMovies, new Comparator<Movie>() { @Override public int compare(Movie o1, Movie o2) { return o1.getMovieName().compareTo(o2.getMovieName()); } }); |
The problem with Anonymous Comparator lies in its syntax. Each time we want to sort a list using a comparator, remembering the bulky syntax becomes necessary.
Generally, the main issue with Anonymous classes is their syntax; even for very simple operations, complex code is required. To address this, JDK introduced a new feature called Lambda Expressions. We will revisit this example after explaining lambda expressions to understand how they can simplify complex code.
4. What is Lambda Expressions?
Lambda expression represents an anonymous function. It comprises of a set of parameters, a lambda operator (->) and a function body . You can call it
function without name.The connection between Lambda Expression and Functional Interface:
One might wonder about the connection between the previously introduced functional interface and Lambda expressions. Lambda expressions can be applied to the abstract method of a functional interface, which is either implemented or instantiated anonymously.
5. Structure of Lambda Expressions
|
1 2 3 4 |
(Argument List) ->{expression;} or (Argument List) ->{statements;} |
So we can divide structure of Lambda expression to three parts:
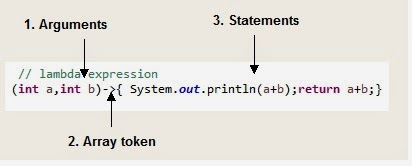
- Argument list or parameters
- Lambda expression can have zero or more arguments.
()->{System.out.println(“Hello”)}; //Without argument, will print hello
(int a)->{System.out.println(a)}; // One argument, will print value of a
(int a,int b)-> {a+b};//two argument, will return sum of these two integers - We can choose to not declare the type of arguments as it can be inferred from context.
-
(a,b)->{a+b}; // two argument, will return sum of these two numbers
- We can not declare one argument’s type and do not declare type for other argument.
-
(int a,b)->{a+b}; // Compilation error
- When there is a single parameter, if its type is inferred, it is not mandatory to use parentheses
a->{System.out.println(a)}; // Will print value of number a
- Lambda expression can have zero or more arguments.
- Array token (->)
- Body
Bodycan have expression or statements.- If there is only one statement in the body, the curly brace is not needed, and return type of the anonymous function is the same as the body expression
- If there is more than one statement, then it should be in curly braces, and return type of the anonymous function is the same as the value return from the code block,
voidif nothing is returned.
Let’s look at some examples, focusing on initializing a thread, and now it will become apparent how lambda expressions can simplify coding:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
public class ThreadSample { public static void main(String[] args) { // old way new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Thread is started"); } }).start(); // using lambda Expression new Thread(()->System.out.println("Thread is started")).start(); } } |
Let’s take another example of Comparator, which we have seen in Anonymous Comparator in Java. We will create a list of movies and sort it by movie name using trivial way and lambda expressions.
Create a class called
Movie.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class Movie { String movieName; long duration; public Movie(String movieName, long duration) { super(); this.movieName = movieName; this.duration = duration; } public String getMovieName() { return movieName; } public void setMovieName(String movieName) { this.movieName = movieName; } public long getDuration() { return duration; } public void setDuration(long duration) { this.duration = duration; } @Override public String toString() { return "Movie Name: " + this.getMovieName() + "|| " + "Movie duration: " + this.getDuration(); } } |
Create a main class called ComparatorMain.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; public class ComparatorLambdaMain { /** * @author Arpit Mandliya */ public static void main(String[] args) { Movie m1=new Movie("Inception",110); Movie m2=new Movie("GodFather",200); Movie m3=new Movie("Forest Gump",130); Movie m4=new Movie("Avengers",150); List<Movie> listOfMovies = new ArrayList<>(); listOfMovies.add(m1); listOfMovies.add(m2); listOfMovies.add(m3); listOfMovies.add(m4); System.out.println("Before Sort by name : "); for (int i = 0; i < listOfMovies.size(); i++) { Movie movie = (Movie) listOfMovies.get(i); System.out.println(movie); } // Sort by movieName // Anonymous Comparator // old way Collections.sort(listOfMovies, new Comparator<Movie>() { @Override public int compare(Movie o1, Movie o2) { return o1.getMovieName().compareTo(o2.getMovieName()); } }); // Using lambda expression Collections.sort(listOfMovies, (o1, o2) -> o1.getMovieName().compareTo(o2.getMovieName())); System.out.println("After Sort by name: "); for (int i = 0; i < listOfMovies.size(); i++) { Movie movie = (Movie) listOfMovies.get(i); System.out.println(movie); } } } |
Before Sort by name :
Movie Name: Inception|| Movie duration: 110
Movie Name: GodFather|| Movie duration: 200
Movie Name: Forest Gump|| Movie duration: 130
Movie Name: Avengers|| Movie duration: 150
After Sort by name:
Movie Name: Avengers|| Movie duration: 150
Movie Name: Forest Gump|| Movie duration: 130
Movie Name: GodFather|| Movie duration: 200
Movie Name: Inception|| Movie duration: 110
Movie Name: Inception|| Movie duration: 110
Movie Name: GodFather|| Movie duration: 200
Movie Name: Forest Gump|| Movie duration: 130
Movie Name: Avengers|| Movie duration: 150
After Sort by name:
Movie Name: Avengers|| Movie duration: 150
Movie Name: Forest Gump|| Movie duration: 130
Movie Name: GodFather|| Movie duration: 200
Movie Name: Inception|| Movie duration: 110
As can be seen here, a lambda expression has been used for the Comparator. Instead of writing an Anonymous Comparator, the expression has been simplified significantly.

Thus, the arguments
o1 and o2 were passed without specifying their types, as these can be inferred from the context. Since there is only one statement, there is no need to enclose it in curly braces.6. HelloWorld Lambda Expression Example
Create an Interface Called HelloWorld
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public interface HelloWorld { void sayHello(); } |
Create a class called HelloWorldMain
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class HelloWorldMain { public static void main(String args[]) { // Lambda Expression HelloWorld helloWorld=()->System.out.println("Hello using Lambda Expression"); helloWorld.sayHello(); } } |
Run above program you will get the following output:
Hello using Lambda Expression
7. Conclusion
In this guide, we took a beginner-friendly look at Lambda expressions in Java. We started with what Functional Interfaces are and then moved on to what Lambda expressions are and how they make coding simpler and cleaner. For example, we saw how they can make sorting a list of movies or creating a new thread much easier than the old ways in Java. With Lambda expressions, you don’t have to write a lot of code for simple tasks. By the end of this article, you should have a basic understanding of Lambda expressions and how they can help you write better Java code. As you keep practicing and using them, you’ll see how handy and powerful they can be!
Was this post helpful?
Let us know if this post was helpful. Feedbacks are monitored on daily basis. Please do provide feedback as that\'s the only way to improve.



Excellent blogs for lambda expression.