Python allows us to work with different data structures and write them to an external file.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to write a list to a file in Python. If you want write list to CSV file, you can refer write list to CSV in Python.
Table of Contents
- Using the write() function to write a list to a file in Python
- Using the writelines() function to write a list to a file in Python
- Using the pickle.dump() function to write a list to a file in Python
- Using the json.dump() function to write a list to a file in Python
- Using the unpack operator * to write a list to a file in Python
- Using the numpy.savetxt() function to write a list to a file in Python
Using the write() function to write a list to a file in Python
The write() function is used to write contents to a file in Python. We use the open() function to create a file object and open it in write mode. We can iterate through the list and write every element individually.
We implement this in the following code.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open(r'Desktop\Manav\Article\sample1.txt', 'w') as f: for item in lst: f.write("%s\n" % item) |
Output
Here is output of the program.
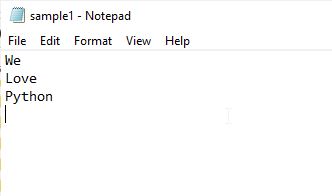
You need to change r'Desktop\Manav\Article\sample1.txt' to the path where you want to write list.
The %s is used to specify that the item is a string and \n adds a new line after every element.
Instead of iterating through the list, we can also use the join() function. The join() function will combine all the elements of the list after separating them with a specified character.
For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open('sample1.txt', 'w') as f: f.write("\n".join(lst)) |
When we open a file in write mode (using w), it clears the contents of the given file. If a file contains some contents and we want to preserve it then we should open the file in append mode.
See the code below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open('sample1.txt', 'a') as f: f.write("\n".join(lst)) |
This way, we start writing the data to the list to the end of the file, without clearing any data which is present earlier.
Further reading:
Using the writelines() function to write a list to a file in Python
The writelines() function is used to write the contents of a list to a file. We can open the file using the open() function in the required mode.
We can open the file in write or append mode in this function.
For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open('sample1.txt', 'w') as f: f.writelines(lst) |
Using the pickle.dump() function to write a list to a file in Python
The pickle module is used to serialize and deserialize objects in Python by converting them to bytes. For this, we use the dump() function in this module. We need to open the file using the open() function as we did in the earlier method.
For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
import pickle lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open(r'Desktop\Manav\Article\sample1.txt', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(lst,f) |
Using the json.dump() function to write a list to a file in Python
The dump() function from the json module works similarly to the one discussed earlier.
See the following code.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
import json lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open('sample1.txt', 'w') as f: json.dump(lst, f) |
Using the unpack operator * to write a list to a file in Python
The unpack operator can be used to unpack an iterable object. In Python 3.5 and above we can use the print() function with the unpack operator to write a list to a file in Python.
We implement this below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
lst = ["We","Love","Python"] with open('sample1.txt', 'w') as f: print(*lst, sep="\n", file=f) |
Using the numpy.savetxt() function to write a list to a file in Python
The savetxt() function can be used to export an array or a list to an external text file. We can specify the format for the string using the fmt parameter, newline character, and even set the delimiter character using the delimiter argument.
We use this function in the following example.
|
1 2 3 4 |
import numpy as np np.savetxt('sample.txt', lst, delimiter="\n", fmt="%s") |
That’s all aboout how to write a list to a file in python.



