Table of Contents
Timer is an utility class which can be used to schedule tasks on specific time or repeatedly.
Lets say, you are developing an banking application and there is need to process the data at 7 PM evening daily. You can easily schedule task using Timer class.
For creating a task, you need to extends TimerTask and Timer can be used to set time for the task.
TimerTask : It is task which will be executed at specific time.
Timer : It is utility class which is used to set time for the task.
Timer class is thread safe , so multiple threads can share one timer object. Timer class internally uses java.util.TaskQueue to manage task internally. Only one thread can execute timer task at a time.
For example:
You are executing task in every 5 secs but actual execution itself is taking 10 seconds, then subsequent task will be added to queue and as soon as current execution completes, it will notify and another thread will start executing the task.
When you debug timer object, it looks something like this.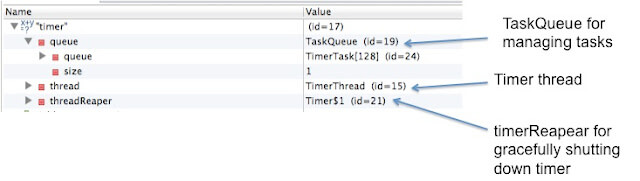
When you debug timer object, it looks something like this.

Methods for scheduling task:
There are several methods in timer class that can be used to schedule.
For one time execution:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay,long period) For example: // it will execute timer task after delay of 5 seconds timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(),5000); |
For repeated execution:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public void schedule(TimerTask task,long delay) For example: // it will execute timer task in every 2 seconds after first delay of 1 second timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(),1000,2000); |
For executing task at particular time:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date time) For example: // Scheduling task at today : 23:13:00 PM Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 23); calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 13); calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0); Date time = calendar.getTime(); timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(timer), time); |
|
1 2 3 |
public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) |
Example:
For one time exectution:
Create a class MyTimerTask.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{ Timer timer; public MyTimerTask(Timer timer) { this.timer=timer; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Executing timer task"); // to stop timer thread timer.cancel(); } } |
In above class, we are using timer.cancel() to stop the timer thread. When you call timer.cancel() method, it completes execution of current thread and discards all other threads which are in queue.
Create a class TimerMain.java.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.util.Timer; public class TimerMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // It will create new thread Timer timer=new Timer(); // task will be scheduled after 5 sec delay timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(timer), 5000); } } |
|
1 2 3 |
Executing timer task |
For repeated execution:
Create a class MyTimerTask.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Executing timer task on "+TimerMain.convertTimeToDateFormat(System.currentTimeMillis())); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Timer; public class TimerMain { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Timer tasks started on "+convertTimeToDateFormat(System.currentTimeMillis())); System.out.println("**************************"); // It will create new thread Timer timer=new Timer(); timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(), 1000,2000); // Stopping the timer thread after some time for example :12 secs. try { Thread.sleep(12000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // you can call timer.cancel() or System.exit(0) System.out.println("**************************"); System.out.println("Timer tasks finished on "+convertTimeToDateFormat(System.currentTimeMillis())); System.exit(0); } public static String convertTimeToDateFormat(long milliseconds) { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("MMM dd,yyyy HH:mm:ss"); Date resultdate = new Date(milliseconds); return sdf.format(resultdate); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
Timer tasks started on Aug 18,2015 22:48:22 ************************** Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:23 Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:25 Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:27 Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:29 Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:31 Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 22:48:33 ************************** Timer tasks finished on Aug 18,2015 22:48:34 |
For executing task at particular time:
Create a class MyTimerTask.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{ Timer timer; MyTimerTask(Timer timer) { this.timer=timer; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Executing timer task on "+TimerMain.convertTimeToDateFormat(System.currentTimeMillis())); // to stop time thread timer.cancel(); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.timer; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Timer; public class TimerMain { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Timer tasks started on "+convertTimeToDateFormat(System.currentTimeMillis())); System.out.println("**************************"); // It will create new thread Timer timer=new Timer(); // Scheduling task at today : 23:13:00 PM Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 23); calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 13); calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0); Date time = calendar.getTime(); timer.schedule(new MyTimerTask(timer), time); } public static String convertTimeToDateFormat(long milliseconds) { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("MMM dd,yyyy HH:mm:ss"); Date resultdate = new Date(milliseconds); return sdf.format(resultdate); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Timer tasks started on Aug 18,2015 23:12:40 ************************** Executing timer task on Aug 18,2015 23:13:00 |
Was this post helpful?
Let us know if this post was helpful. Feedbacks are monitored on daily basis. Please do provide feedback as that\'s the only way to improve.



Hi. Nice post. Do you think https://www.udemy.com/java-interview-guide/ is worth?