In Python, one can perform many kinds of tasks including mathematical operations like add, subtract, divide, dealing with matrices, etc. Besides all these operations, one can also perform complex mathematical operations like dealing with sets and matrices, trigonometric operations using many libraries and modules provided by Python.
In this tutorial, we will see how to find out the inverse sine in Python.
Table of Contents
Use the numpy.arcsin Function of the NumPy Library
The NumPy library is a widely used library in Python. This library helps in dealing with arrays, matrices, linear algebra, and Fourier transform. NumPy stands for Numerical Python.
The NumPy has a function known as the arcsin() function that is a mathematical function used to calculate the inverse sine of elements in an array.
Some Parameters of the numpy.arcsin() function
x (array)– This parameter defines the input array of which the inverse sine values are to be found.out (array, None, or tuple)– This parameter defines the location in which the result is stored. If this parameter is not defined then the result is returned in a new array.
There are many other parameters like where (array), casting, order, etc. Also, note that only the x (array) parameter is necessary to define. All the other parameters are optional.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import numpy as np input_array = [-1, 0, 0.3, 0.6, 1] print ("Input Array :", input_array) arcsin_Values = np.arcsin(input_array) print ("Inverse Sine values :", arcsin_Values) |
Output:
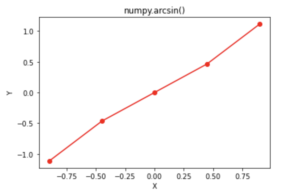
Graphical Representation of the numpy.arcsin() function.
In this program, the Matplotlib library is used to plot the graph. This library is a very good library when it comes to data visualisation in python.
In the program below, the linspace() function of the NumPy is used. The linspace() function helps in creating a random numerical sequence that are evenly spaced.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt input_array = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 15) output_array = np.arcsin(input_array) print("input_array :", input_array) print("output_array with arcsin :", output_array) plt.plot(input_array, output_array,color = 'red', marker = "o") plt.title("numpy.arcsin()") plt.xlabel("X") plt.ylabel("Y") plt.show() |
Output:
-0.44879895 0. 0.44879895 0.8975979 1.34639685 1.7951958
2.24399475 2.6927937 3.14159265] output_array with arcsin : [ nan nan nan nan nan -1.11428969
-0.46542088 0. 0.46542088 1.11428969 nan nan
nan nan nan]
Use the math.asin() Function of the Math Library
Python’s Math library helps in performing complex mathematical problems by providing different mathematical constants and functions in Python.
The asin() function of the Math library is also used for calculating the inverse sine value (between -1 to 1) of a given input value in Python.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
import math print (math.asin(-1)) print (math.asin(0)) print (math.asin(0.3)) print (math.asin(0.6)) print (math.asin(1)) |
Output:
0.0
0.30469265401539747
0.6435011087932844
1.5707963267948966
Use the sympy.asin() Function of the SymPy Library
Python’s SymPy library is used in symbolic mathematics. It is a Computer Algebra System (CAS) that provides short and precise codes that can be used easily by the user.
The asin() function of the SymPy library is also used for calculating the inverse sine value of a given input value in Python.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
from sympy import * input_value = asin(1) print(input_value) |
Output:
That’s all about how to get inverse sine in Python.