Table of Contents
Exceptions
I have started writing about the Java Certification and how to prepare for the various topics related to OCAJP exams in my blog. In my previous post, I have published few sample mock questions for StringBuilder class.
In this post I am going to explain about the another OCAJP exam objective “Differentiate among checked exceptions, unchecked exceptions, and Errors”. This is exam objective 8.1 in both [OCAJP 8](https://java2blog.com/cracking-java-certification-ocajp-8-with-whizlabs/ “OCAJP 8”) and OCAJP 7 exams. There is no difference between both the exams with respect to this objective.
OCA exam would test your knowledge on the exceptions that are available in Java SE 6 version. There is no revision of latest versions in the OCA exam. But, OCP exam covers the latest exception handling mechanism from the versions Java SE 7 & 8.
In this Post we would explain about exception hierarchy, difference between checked, unchecked exceptions and errors.
If you are looking for mock exams to practice OCAJP exam, you can try these practice questions for OCAJP 8 exam.
What is Exception ?
- Java doc says “ An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions.”
- The term “exception” means “exceptional condition” and is an occurrence that changes the normal program flow.
- A bunch of things can lead to exceptions, including hardware failures, resource exhaustion, and good old bugs.
- When an exception event occurs in Java , an exception is said to be “thrown”.
- The code that is responsible for doing something about the exception is called an “exception handler” and it “catches” the thrown exception.
- Every Exception will be thrown at runtime.
Exceptions hierarchy
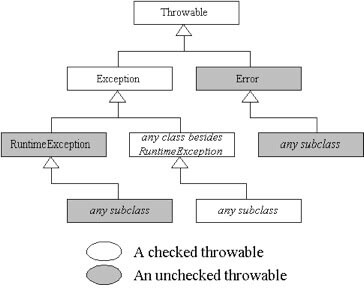
Throwable
- Throwable class is present in java.lang package.
- Throwable is the super class for all exception classes in Java.
- It has two direct sub classes such as Exception, Error(Of Course every exception class is directly or indirectly sub class of Throwable ).
- It has some methods which are to print exceptions details as per application requirement.
Exception
- Exception is the class present in java.lang package.
- This class doesn’t have it’s own methods , it inherited methods from Throwable class.
- All sub classes of this class are considered as checked Exceptions(except RuntimeException and it’s sub classes).
RuntimeException
- RuntimeException is the class present in java.lang package.
- It is sub class of Exception class.
- This class is also doesn’t have it’s own methods , it inherited methods from Throwable class. Because Throwable is indirectly super class of RuntimeException.
- All sub classes of this class are considered as unchecked Exceptions.
Error
- Error is the class present in java.lang package.
- It is sub class of Throwable class.
- This class is also doesn’t have it’s own methods , it inherited methods from Throwable class. Because Throwable is indirectly super class of RuntimeException.
- All sub classes of this class are considered as unchecked errors.
Checked Exceptions
- If a class is a subclass of Exception class directly or indirectly and should not be subclass of RuntimeException class, it is a checked exception.
- Why the name checked, because these exceptions can be detected at compile time.
- Of course checked exceptions thrown at runtime,It is mandatory that Java code requires to declare or handle them at compile time otherwise the code doesn’t compile .
- These are caused by unexpected conditions outside control of code (e.g. database down, file I/O error, wrong input, etc).
- These are thrown programmatically.
- These are recoverable errors.
- For Example IOException is a checked exception, it occurs when you are try to open a file which is not existed in that location.
- You can recover from this exception by putting the file in the same location.
OCAJP checked exceptions
FileNotFoundException thrown programmatically when code tries to reference a file that does not exist
IOException Thrown programmatically when there’s a problem reading or writing a file.
For the OCA exam, you only need to know that these are checked exceptions. Also keep in mind that FileNotFoundException is a subclass of IOException, although the exam will remind you of that fact if it comes up. You’ll see these two exceptions in more detail on the OCP exam.
Unchecked Exceptions
- If a class is a subclass of RuntimeException class directly or indirectly, it is a unchecked exception.
- Why the name unchecked , because these are not detected at compile time. So, It is not mandatory that Java code requires to declare or handle them.
- These are also thrown at run time.
- These are thrown by JVM.
- These are also recoverable errors.
- For Example : when you call method on [reference variable](https://java2blog.com/reference-variable-java/ “reference variable”) which is null causes NullPointerException.
- You can recover from this exception , by checking reference is null or not before method on that reference.
OCAJP unchecked Exceptions
ArithmeticException
• It is Thrown by the JVM when code attempts to divide by zero.
Example :
|
1 2 3 4 |
int b= 9; int c = b/0; |
Running this code results in the following output: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- It is thrown by the JVM when code uses an illegal index to access an array.
- Example :
1234int[] a = new int[2];System.out.println(a[-1]) - This is a problem because there’s no such thing as a negative array index. Running this code givess the following output: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: -1
ClassCastException
- It is thrown by the JVM when an attempt is made to cast an exception to a subclass of which it is not an instance
- Example :
12345String type = "OCAJP8";Object obj = type;Integer number = (Integer) obj; - The compiler sees a cast from Object to Integer. This could be okay. The compiler doesn’t realize there’s a String in that Object. When the code runs, it gives the following output: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.String cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer
IllegalArgumentException
- It is thrown by the programmer to indicate that a method has been passed an illegal or inappropriate argument.
- Example :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
public static void setCount(int count) { if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("cont must not be negative"); this.count = count; } |
- The program throws an exception when it’s not happy with the parameter values. The output looks like this: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: count must not be negative
NullPointerException
-
- It is thrown by the JVM when there is a null reference where an object is required.
- Example :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
String name; public void printLength() throws NullPointerException { System.out.println(name.length()); } |
- Running this code results in this output: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NullPointerException
NumberFormatException
[NumberFormatException](https://java2blog.com/java-lang-numberformatexception/ “NumberFormatException”) is thrown by the programmer when an attempt is made to convert a string to a numeric type but the string doesn’t have an appropriate format.Example :
|
1 2 3 |
Integer.parseInt("OCA"); |
Errors
- If a class is a subclass of Error class directly or indirectly,it is an error.
- For Errors, It is not mandatory that Java code requires to declare or handle them. If you catch there won’t be compile time error. But you shouldn’t catch it.
- These are thrown by JVM.
- These are unrecoverable errors.
- For Example when you try to create infinite objects you will get OutOfMemoryError .
- You can’t recover from these errors.
ExceptionInInitializerError
- It is thrown by the JVM when a static initializer throws an exception and doesn’t handle it.
- Example :
12345678static {int[] c = new int[3];int num = c[-1];}public static void main(String[] args) { } - This code gives information about two exceptions: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError Caused by: java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: -1
- We get the ExceptionInInitializerError because the error happened in a static initializer.
- That information alone wouldn’t be particularly useful in fixing the problem. Therefore, Java also tells us the original cause of the problem: the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException that
- We need to fix the ExceptionInInitializerError is an error because Java failed to load the whole class. This failure prevents Java from continuing.So the errors are unrecoverable.
StackOverflowError
- It is thrown by the JVM when a method calls itself too many times (this is called infi nite recursion because the method typically calls itself without end).
- Example :
123456public static void call(int n){call(8);} - The output contains this line: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.StackOverflowError
- Since the method calls itself, it will never end. Eventually, Java runs out of room on the stack and throws the error. This is called infinite recursion.
NoClassDefFoundError
It is thrown by the JVM when a class that the code uses is available at compile time but not runtime. This error won’t show up in code on the exam—you just need to know that it is an error.
Difference between checked exception, unchecked exception and errors
|
Parameter
|
Checked Exception
|
Unchecked Exception
|
Error
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
How to recognise
|
sub class of Exception class
|
sub class of RuntimeException class
|
sub class of Error class
|
|
Good to
catch |
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Is Program required to handle or declared
|
Yes
|
No
|
No |
|
Thrown by
|
Programatically
|
JVM |
JVM
|
|
Recoverable
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Example
|
IOException
FileNotFoundException etc |
NullPointerException
ClassCastException etc |
StackOverFlowError
OutOfMemoryError etc |
For the OCAJP exam preparation, for this exam objective you have to concentrate on the below areas.
Conclusion
• What are common exception classes?
• How they occur?
• When they occur?
• How will it be thrown?
Also practice lot of sample mock questions to get familiar with the concepts. That is very important for you to get the confidence for attending the real exam.
Good luck for your exam preparation!!
References
If you are preparing for the [OCAJP certification](https://java2blog.com/cracking-java-certification-ocajp-8-with-whizlabs/ “OCAJP certification”) exam, the following references would be much useful.
• OCAJP 8 Exam Curriculum
• OCAJP Forums
• How to prepare for OCAJP Exam?
• What are the good books available for OCAJP 8 exam?


