Table of Contents
In this post, we will see about static keyword in java.So static keyword can be associated with:
- Variable
- Method
- Block
- Nested class
Lets go through each one by one.
Static variable:
If any instance variable is declared as static.It is known as static variable.
|
1 2 3 |
static int countryCounter; |
- Static variable belongs to a class not to a object.
- Static variable are initialized only once in class area at the time of class loading
- All objects share single copy of static variable
- You don’t need to create object to access static variable.You can directly access it using class name.
- Static variable can be accessed by instance java methods also.
If you create a class with two variables, one static, one non static.Non static variable of that class (objects created from that class) gets its own version of that variable. But with the static variable, it belongs to the class, and there is only one. Although any object from that class can reference it.
Example:
Lets take a very simple example.You want to track how many objects you have created.For that you have a static variable in your class.Lets say your class is:
Country.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; /* * @author:Arpit Mandliya */ public class Country { //static variable static int countryCounter; // instance variable String name; int dummyCounter; Country(String name) { this.name=name; countryCounter++; dummyCounter++; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("****************************************"); Country india=new Country("India"); System.out.println("Country Name: "+india.getName()); System.out.println("Number of country object created: "+Country.countryCounter); System.out.println("Dummy counter not a static variable: "+india.dummyCounter); System.out.println("****************************************"); Country france=new Country("France"); System.out.println("Country Name: "+france.getName()); System.out.println("Number of country object created: "+france.countryCounter); System.out.println("Dummy counter not a static variable: "+france.dummyCounter); System.out.println("****************************************"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } |
Output:
When you run above program,you will get following results:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
**************************************** Country Name: India Number of country object created: 1 Dummy counter not a static variable 1 **************************************** Country Name: France Number of country object created: 2 Dummy counter not a static variable 1 **************************************** |
Diagram:
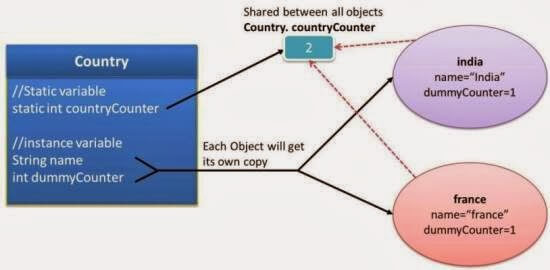
In above example,we have one static variable named “countryCounter” so whenever we are creating one new object,its value will be incremented by 1 as counterCounter variable is being shared by all country objects and we have instance variable named “dummyCounter” so whenever any new object is created,its value is initialized to 0 again.
Static Method:
If any method is declared as static.It is known as static method.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public static void printCountryCounter() { System.out.println("Number of country object created: "+countryCounter); } |
- Static method belongs to a class not to object.
- Static method can be invoked directly using a className.Although It can be invoked using objectName also
- Generally static method are used for getting static fields.
- You can access static methods through java instance methods.
- You can not access non static method or instance variable in static methods.
- A static method can not refer to this or super keyword.
We will create above example and will use one static method printCountryCounter for printing countryCounter variable.
Country.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; /* * @author:Arpit Mandliya */ public class Country { String name; static int countryCounter; int dummyCounter; Country(String name) { this.name=name; countryCounter++; dummyCounter++; } public static void main(String[] args) { Country india=new Country("India"); System.out.println("****************************************"); System.out.println("Country Name: "+india.getName()); printCountryCounter(); System.out.println("Dummy counter not a static variable: "+india.dummyCounter); System.out.println("****************************************"); Country france=new Country("France"); System.out.println("Country Name: "+france.getName()); printCountryCounter(); System.out.println("Dummy counter not a static variable: "+france.dummyCounter); System.out.println("****************************************"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public static void printCountryCounter() { System.out.println("Number of country object created: "+countryCounter); } } |
When you run above program,you will get following results:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
**************************************** Country Name: India Number of country object created: 1 Dummy counter not a static variable 1 **************************************** Country Name: France Number of country object created: 2 Dummy counter not a static variable 1 **************************************** |
Why can’t you access non static member from static method:
When you call non static method from static method,you will get compilation error.
For example:In above printCountryCounter(),Lets say you call getName()
You will compilation error.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
public static void printCountryCounter() { getName(); //Compilation error System.out.println("Number of country object created: "+countryCounter); } |
Static block:
- Static blocks are used to initialize static data members.
- Static blocks get executed before main method get executed.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; public class StaticBlockExample { /** * @Author:Arpit Mandliya */ static{ System.out.println("This block will get call before main method"); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("In main method"); } } |
When you run above program,you will get following results:
|
1 2 3 4 |
This block will get call before main method In main method |
Static class:
- Nested static class does not need reference of outer class.
- A static class cannot access non-static members of the Outer class. It can access only static members of Outer class including private.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; /* * @author:Arpit Mandliya */ public class OuterClass { static class InnerStaticClass{ public void printInnerClass() { System.out.println("In inner class"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("****************************************"); OuterClass.InnerStaticClass inc=new OuterClass.InnerStaticClass(); inc.printInnerClass(); System.out.println("****************************************"); } public static void printOuterClass() { System.out.println("In outer class"); } } |
When you run above program,you will get following results:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
**************************************** In inner class **************************************** |


