Table of Contents
In this post, we will see about Strategy design pattern in java.
Strategy design pattern allows us to change algorithm implementation at runtime.Strategy design pattern provides multiple algorithms and client can choose algorithm based on their needs with the help of composition.
Strategy design pattern example
Let’s understand this with the help of simple example.
Let’s say you want to implement multiple sorting algorithms.
You need to sort list based on input sorting type(Merge sort and Quick sort).Please note that there should be provision to add new sorting type in future.
Create an Enum called "SortingType.java" as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; public enum SortingType { MERGE_SORT,QUICK_SORT; } |
Create Service class named SortingManager as below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; import java.util.List; public class SortingManager { List list; public SortingManager(List list) { super(); this.list = list; } public void sortListBasedOnType(SortingType sortingType) { System.out.println("==================================="); System.out.println("Sorting List based on Type"); System.out.println("==================================="); if("MERGE_SORT".equalsIgnoreCase(sortingType.toString())) { sortListUsingMergeSort(); } else if("QUICK_SORT".equalsIgnoreCase(sortingType.toString())) { sortListUsingQuickSort(); } } private void sortListUsingMergeSort() { System.out.println("Sorting List using merge sort"); } private void sortListUsingQuickSort() { System.out.println("Sorting List using quick sort"); } } |
Create a main class named "SortingMain.java" which will call SortingManager to sort list.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class SortingMain { public static void main(String[] args) { List list = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{44,5,3,5,5,64,3}); SortingManager sm=new SortingManager(list); // Sorting using merge sort sm.sortListBasedOnType(SortingType.MERGE_SORT); System.out.println(); // Sorting using quick sort sm.sortListBasedOnType(SortingType.QUICK_SORT); } } |
Output:
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using merge sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using quick sort
As you can see, this is simple code which is working fine.You have tested code and found out that you are able to sort list based on sorting type.
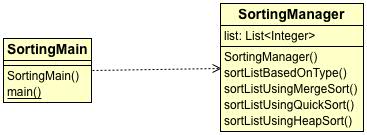
Now you need to create one more sorting type i.e. Heap sort.If you notice, you need to make changes as below:
1) You need to make changes in Enum SortingType.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; public enum SortingType { MERGE_SORT,QUICK_SORT,HEAP_SORT; } |
2) You need to make changes in SortingManager class which you have already tested.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; import java.util.List; public class SortingManager { List list; public SortingManager(List list) { super(); this.list = list; } public void sortListBasedOnType(SortingType sortingType) { System.out.println("==================================="); System.out.println("Sorting List based on Type"); System.out.println("==================================="); if("MERGE_SORT".equalsIgnoreCase(sortingType.toString())) { sortListUsingMergeSort(); } else if("QUICK_SORT".equalsIgnoreCase(sortingType.toString())) { sortListUsingQuickSort(); } else if("HEAP_SORT".equalsIgnoreCase(sortingType.toString())) { sortListUsingHeapSort(); } } private void sortListUsingMergeSort() { System.out.println("Sorting List using merge sort"); } private void sortListUsingQuickSort() { System.out.println("Sorting List using quick sort"); } private void sortListUsingHeapSort() { System.out.println("Sorting List using heap sort"); } } |
Now you can sort list using heap sirt as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.designpattern; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class SortingMain { public static void main(String[] args) { List list = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{44,5,3,5,5,64,3}); SortingManager sm=new SortingManager(list); // Sorting using merge sort sm.sortListBasedOnType(SortingType.MERGE_SORT); System.out.println(); // Sorting using quick sort sm.sortListBasedOnType(SortingType.QUICK_SORT); System.out.println(); // Sorting using heap sort sm.sortListBasedOnType(SortingType.HEAP_SORT); } } |
Output:
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using merge sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using quick sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using heap sort
As you can see, we have to modify at many places which we have already tested and we need to retest all the functionalities again.
Strategy pattern example
Let’s see how Strategy pattern will be able to solve the problem.
Create SortingManager.java as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.List; public class SortingManager { SortingStrategy sortingStrategy; List<Integer> list; public SortingManager(List<Integer> list,SortingStrategy sortingStrategy) { super(); this.list = list; this.sortingStrategy=sortingStrategy; } public void sortList() { System.out.println("==================================="); System.out.println("Sorting List based on Type"); System.out.println("==================================="); sortingStrategy.sort(list); } public SortingStrategy getSortingStrategy() { return sortingStrategy; } public void setSortingStrategy(SortingStrategy sortingStrategy) { this.sortingStrategy = sortingStrategy; } public List<Integer> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<Integer> list) { this.list = list; } } |
Create an interface called SortingStrategy as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.List; public interface SortingStrategy { void sort(List<Integer> list); } |
Create a class named "MergeStrategy.java" for sorting using merge sort.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.List; public class MergeSortStrategy implements SortingStrategy { @Override public void sort(List list) { System.out.println("Sorting List using merge sort"); } } |
Create a class named "QuickSortStrategy.java" for sorting using quick sort.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.List; public class QuickSortStrategy implements SortingStrategy { @Override public void sort(List list) { System.out.println("Sorting List using quick sort"); } } |
Let’s create a main class SortingMain.java now.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class SortingMain { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{44,5,3,5,5,64,3}); MergeSortStrategy mergeSortStrategy=new MergeSortStrategy(); SortingManager sm=new SortingManager(list,mergeSortStrategy); sm.sortList(); System.out.println(); QuickSortStrategy quickSort=new QuickSortStrategy(); sm.setSortingStrategy(quickSort); sm.sortList(); } } |
Output:
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using merge sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using quick sort
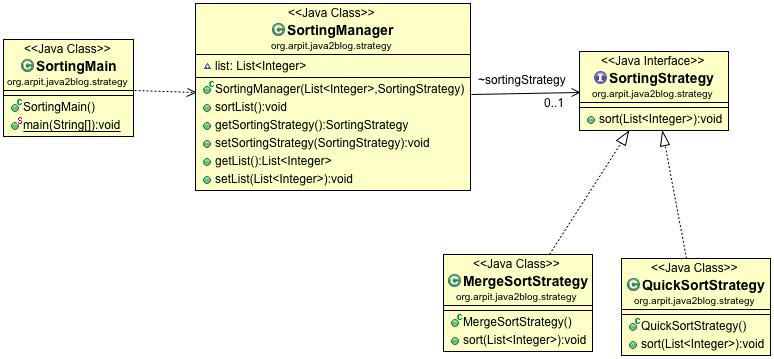
Let’s say you want to sort using heap sort.You need to create below changes:
Create another class named "HeapSortStrategy.java" as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.List; public class HeapSortStrategy implements SortingStrategy { @Override public void sort(List list) { System.out.println("Sorting using heap sort"); } } |
Change in SortingMain.java to add calling code.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package org.arpit.java2blog.strategy; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class SortingMain { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{44,5,3,5,5,64,3}); MergeSortStrategy mergeSortStrategy=new MergeSortStrategy(); SortingManager sm=new SortingManager(list,mergeSortStrategy); sm.sortList(); System.out.println(); QuickSortStrategy quickSort=new QuickSortStrategy(); sm.setSortingStrategy(quickSort); sm.sortList(); System.out.println(); HeapSortStrategy heapSort=new HeapSortStrategy(); sm.setSortingStrategy(heapSort); sm.sortList(); } } |
Output:
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using merge sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting List using quick sort===================================
Sorting List based on Type
===================================
Sorting using heap sort
As you can see, we did not make any changes SortingManager which was already tested.We just added new class "HeapSortStrategy" which enabled us to sort using Heap sort.